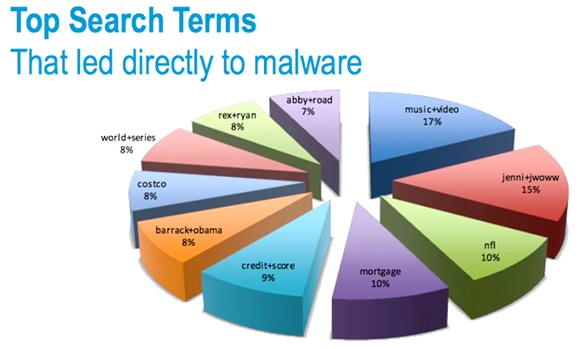
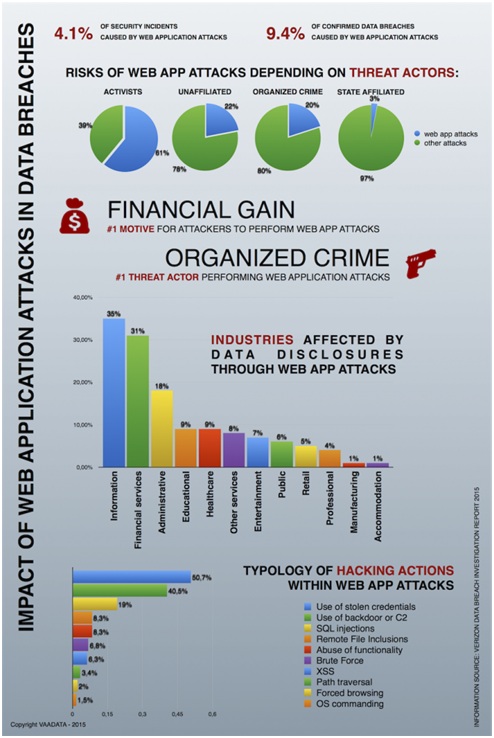
While there is no precise way to stop cyber incidents, cyber security threats and persistent advanced threats are always headline news. The public concerns as well as government domains face some serious troubles posed by the targeted cyber security attacks. There have been cyber incidents that have brought severe loss of sensitive data, information and reputation to organizations.
The cyber security incidents vary in size of the attack. Malware, hacking and social engineering can cause troublesome for small and medium businesses. Targeted attacks covert from major organized sectors can cause widespread disruptions seems major concerns. A fundamental requirement to stay safe compels the organizations to remain informed and will be able to remain safe.
The Top Cyber Security Breach Incidents from 2005 to 2015
| Year | Organization | Incident Classification | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | CardSystems Solutions | SQL Trojan was used to steal data via FTP. Lack of data encryption made it easy. | 40 million credit card accounts exposed. CSS ultimately was forced to sell itself. |
| 2006 | TJX Companies, Inc. | Lack of firewall and data encryption | 94 million credit card details exposed |
| 2006 | The Department of Veterans Affairs (USA) | Human negligence had led to the loss of a laptop and external hard disk. The data was not encrypted on both devices. | A National database of names, dates of births, Social Security numbers, disability ratings of nearly 27 million veterans and active military personnel was stolen. |
| 2006 | AOL | Human negligence | Posted online data of 20+ million web inquiries, including banking details of 650K users |
| 2007 | Monster.com | Phishing scam by hackers from Ukraine. | Sensitive information of 1.3 million job-seeking professionals was stolen. Hackers have sent scam e-mails and infected PCs with malicious software. They threatened to delete all the files on PC unless the victims paid them. |
| 2007 | Fidelity National Information Services
(USA) |
Employee sold data | An employee stole 2.3 million customer records, including banking, credit card and personal information and sold it to Russians and Estonians. |
| 2008 | Heartland Payment Systems | SQL vulnerabilities exploited to inject a spyware | 134 million credit card details exposed |
| 2008 | National Archive and Records Administration
(USA) |
NARA sent a hard drive to a government contractor to fix it and it was declared unusable. NARA did not destroy the drive itself and sent for repair but the drive was not fixed and sent it for trash. | Personal records, including social security number of over 76 million US veterans were left vulnerable. |
| 2009 | Google and many other Silicon Valley corporations | The Chinese hackers exploited a vulnerability of Internet Explorer and accessed Google’s internal network. | The Unknown amount of intellectual property was stolen from Google. They decided to stop operating in China. |
| 2010 | Stuxnet | Top-notch Targeted attack until today, a large-scale breach that began in 2007 and was found in 2010 | Meant to attack Iran’s nuclear power program, but will also serve as a template for real-world intrusion and service disruption of power grids, water supplies or public transportation systems. |
| 2010 | Gawker Media | Lack of password encryption and use of the same passwords on other accounts | Source code of custom-built CMS breached. E-mail addresses and passwords of 1.3 million comment posters stolen. |
| 2010 | Wikileaks | Wiki leaks released U.S. military classified information on the web | Apart from all other information, 90K classified of Afghanistan war and 400K classified military documents of the Iraq war went public. |
| 2011 | Epsilon | Classification – Unidentified incident lead to phishing scams and innumerable identity theft claims. | Information stored in 108 retail stores, major financial firms, non-profit educational institutes and college Board have been breached. Estimated loss of $4 billion. |
| 2011 | RSA Security | Two hacker groups were working for a foreign government and launched phishing attacks against RSA | 40 million records, including employee records were stolen |
| 2011 | PlayStation Network of Sony | Lack of encryption and not enough cyber security enabled. | 77 million accounts hacked and 12 million unencrypted credit card numbers stolen. The Web site was down for over a month and that lead to loss in millions. |
| 2011 | ESTsoft | From Chinese IP addresses the attackers uploaded malware on server to update ALZip compression, an application used by ESTsoft | Biggest South Korean breach where personal information of 35 million people hacked. |
| 2011 | Fidelity National Information Services | The Malware used to exploit network intrusions | Data worth over $100 million is anticipated to have been stolen |
| 2013 | Target Stores | Payment card reader hacked | 40 million credit and debit card numbers stolen, 70 million personal records taken away.. |
| 2014 | Home Depot | Use of malware disguised as anti-virus hacked point-of-sale. | 56 million credit and debit card records stolen. |
| 2015 | Anthem | Cyber attack or hack, the investigation is still ongoing. | 88+ million records of personal information and credit card information stolen. |
A survey conducted by the Global State of Information Security in 2015 among 9700 IT security and business executives in 154 countries- an Outcome from the survey:
- There was a 66% rise in the Information security incidents since 2009.
- Security incidents have risen by 48% since 2013.
- On an average, there are 117,339 cyber security threats happen on a daily basis.
Threat Incident Classification Patterns Used by Cyber Attackers
Find out how to stay safe from cyber threat incidents. The top ten-cyber security incidents classification patterns used by cyber attackers are recognized by the cyber security experts listed here.
1. Negligent behavior
Human negligence is being rated as one of the top most gateways of cyber security vulnerabilities. There have been enough incidents of negligence in the past. A simple mistake committed due to negligence can lead to unimaginable amounts of compromise on security. Negligence can cause via
- Posting the sensitive private or pubic data online,
- Sending information via email or courier to a wrong recipient,
- Disposing of documents or information drives without being cautious.
While no industry is secure from human negligence, usually the public sector, education, administration and healthcare industry suffer from such negligent behavior.
2. Malware Crimes
Malware covers a broad range of threats used to compromise individual systems, servers and desktops. Malware crimes also include the phishing scams. Public sector, information storing cloud servers, utilities and manufacturing industry are preferred target of malware frauds.
3. Web Apps
The cyber security incidents take place due to vulnerability in a web app being used on the e-commerce site or a customized Content management system. Most of these attacks are in use to steal financial data, such as banking or credit card details.
4. Privilege Misuse by Authorized Personnel
An insider or authorized personnel misuses the authority to seize sensitive information and disperses it for a personal gain to the outside market. Study shows that 85% of the personnel use the corporate LAN to misuse privileged information.
BYOD/BYOT is a massive factor that has misused privileges. A survey conducted by Dell, 24% employees have admitted misuse of personal mobile devices or removing security of the operating system from personal device lead to security breaches.
5. Physical Theft
Loss of the device due to negligence or theft has shocking effects. Individuals forget their device at different places like
- Mobile device left behind in a taxi
- Flash drives forgotten in office
- Thumb drives misplaced at unknown places or even forgot them in the pocket of clothes given for laundry
- Actual theft along with other assets, the devices that carried sensitive data were stolen as well
These are some very common scenarios where the devices carrying sensitive data have gone missing. According to Verizon, 43 percent of the device theft takes place within the office premises.
6. Point of Sale or Financial Transaction Intrusions
The Sole purpose of the financial transaction intrusion or point of sale intrusion is to capture the sensitive financial information. Bank details, credit and debit card information, etc. can be stolen, either sold or misused. More than 85 percent of these attacks usually go undetected for weeks.
7. Service Denial Attacks
Service denial attacks otherwise also known as “botnets” are actual target attacks. They are designed to bring the entire functional system of the target to come to a halt. On a small scale, it can hijack an entire website and makes it offline. On a bigger scale, as we saw above in the case of data theft from Monster.com, many victims can be targeted at the same time by taking control of their device.
Service denial attacks are the worst of all kinds since it means target have got no other option then to surrender to the attackers. Apart from being the worst of its kind, these kinds of attacks have grown at a massive rate of 115 percent.
8. Cyber spying
Cyber espionage or cyber spying is usually done to gain inside information from government portals. Gaining military intelligence is usually the primary purpose of such cyber security incidents. Cyber spying is used to access information from the sources where the big data is stored.
How can You Stay Safe from Cyber Threat Incident?
- Do not make excuses: Lack of fund seems poor excuse for compromised security. You will never leave your house or your store open for a theft. Why leave your cyber assets vulnerable? Invest in proper tools such an anti-virus, firewall, SSL certificates, etc. to ensure ample of the safety of your cyber assets.
- Be vigilant: Realizing that your cyber assets have been compromised when a customer logs a complaint not only impacts bad impression, it proves that your organization is not dependable. The Safety of your cyber store and all the data therein is your responsibility.
- Encrypt all sensitive data using a strict encryption method. Never leave sensitive data on mobile devices.
- Educate yourself and your people: Conduct training at regular intervals to educate your staff on how they must remain vigilant and pro-active to keep the organization and its assets safe. Learn to spot attacks and encourage your staff to report any discrepancy noticed by them.
- Limit access: Keep limited data on devices. Only data that is required for the functions should be available, only to the authorised people on “need to know” basis. Limit access to sensitive data as per rank. When someone is fired or roles are changed, implement the changes of limit access before announcing it to the respective people.
- Act promptly: Keep your anti-virus definitions up to date. Never-ever let down all guards at the same time. As soon as you receive information of discrepancy, act promptly on it.
- Two-step authentication: Reduce the risk of theft and damage via stolen credentials by implementing strong passwords and two-step authentication.
When cyber security needs to be implemented online, the physical assets must be secured effectually as well. Keep external hard drives, backup drives, mobile devices such as thumb drive in safe with passwords. Enable self-destruction software or user lockout on input of incorrect credential on the mobile devices and secure the back up drives.