When a browser makes the HTTPS connection, an initial request page takes a little time while the following refresh of the page takes very negligible time. There are some reasons for the slow loading time of HTTPS site and there are specific solutions given here.
In SSL handshake, there are few TCP level round-trips needed to establish HTTPS connections and this process requires some extra bytes during the handshake.
OCSP and CRL can be an issue for slowing website loading time as their performance generally is not adjusted. The CA takes 300 ms (milliseconds) in answering to an OCSP request means the website will take an extra third part of a second in establishing a connection. Even most CAs has not preferred IPv6 for CRL and OCSP servers.
In the past, some of the CAs were desired to remove the entire verification, but it can put SSL in trouble as there will be less reliability if the entire verification would be missing.
The other reason is that SSL certificates carry a number of intermediate certificates that also enhance the volume of data to be exchanged during initial handshake.
Apart from the above, the level of utilized hardware, software, static content ratio, session length, caching behavior also affects SSL performance.
Fact:
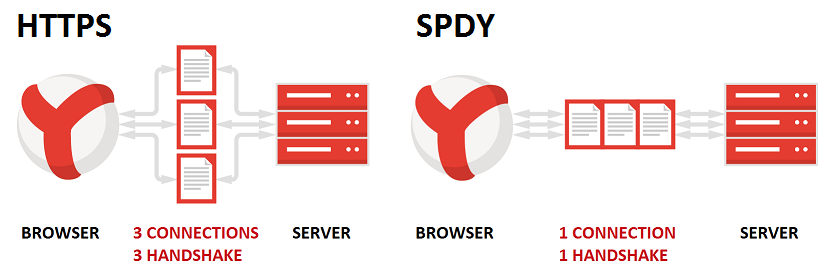
The website owner can take help of SPDY, which is an open network protocol developed by Google that reduces web page loading time.
The efforts of CPU resources can be reduced by compressing textual content or you can upgrade the processor so that it can easily support data encryption task.
With the evolving technology and modern servers has decreased the SSL overhead. Even many Certificate authorities are working closely on CRL and OCSP response time to minimize it up to 100 ms (milliseconds) or less.
Another option is to shorten the intermediate chain in SSL certificate as it takes extra bytes and time.