Certificate Authority Authorization (CAA) DNS Record: Detailed Guide on How to Add, Edit, Or Create it
The effectiveness of web security relies on the Secure Socket Layer certificates. SSL certificates, which apply the Public Key Infrastructure approach, cryptographically secure websites by allowing only the intended recipients to decrypt a given kind of encrypted communication. The web’s Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) has faced austere compromises in recent years that have called for the inclusion of critical security contrivances over the years. One such approach taken to curb PKIs compromises is the Certificate Authority Authorization (CAA) DNS records.
CAA technology gives the domain name owner freedom to create a DNS CAA record that states which Certification Authorities, if there are any, are permitted to issue certificates for the said domain. CAA is so useful as it can significantly reduce a series of certificate miss-issuances that might result from malicious individuals’ mistakes or deeds.
What Is a CAA DNS Record?
A CAA DNS record specifies the Certificate Authorities (CA), who can issue a specific domain name certificate. The record is like a domain holder’s declaration about the CAs authorized to issue an SSL certificate to a particular domain name. Therefore, the record gives Certificates Authorities the ability to find out by themselves whether they are authorized to issue a certificate for your domain. CAA DNS records are so vital; no wonder we are witnessing their increased use. Apart from just declaring who can give a certificate to the domain name, the CAA record also provides the means to indicate the notification guidelines in a situation where someone requests a certificate from a CA that has not been authorized to do so.
In the absence of a CAA DNS record, any Certificate Authority is free to issue a certificate on the domain. On the other hand, the presence of a CAA record means that only the Certificate Authorities listed on the record will be allowed to issue a certificate for the said domain. The CAA DNS record also sets policies for the whole domain or a particular hostname. It is also vital to note that, unless overridden, a CAA record for the main domain will cut across all its subdomains. For instance, a CAA record for www.domain.com will apply to its subdomains, like login.domain.com and blog.domain.com. The CAA DNS records usually control the issuance of both wildcard SSL certificates and single SSL certificates.
What Happens When No CAA Record Is Found?
When a CAA record is not found, a malicious hacker can quickly generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) for your domain and have the certificate signed by any domain. This is a security threat that you should not allow to happen.
What Does A DNS CAA Record Look Like?
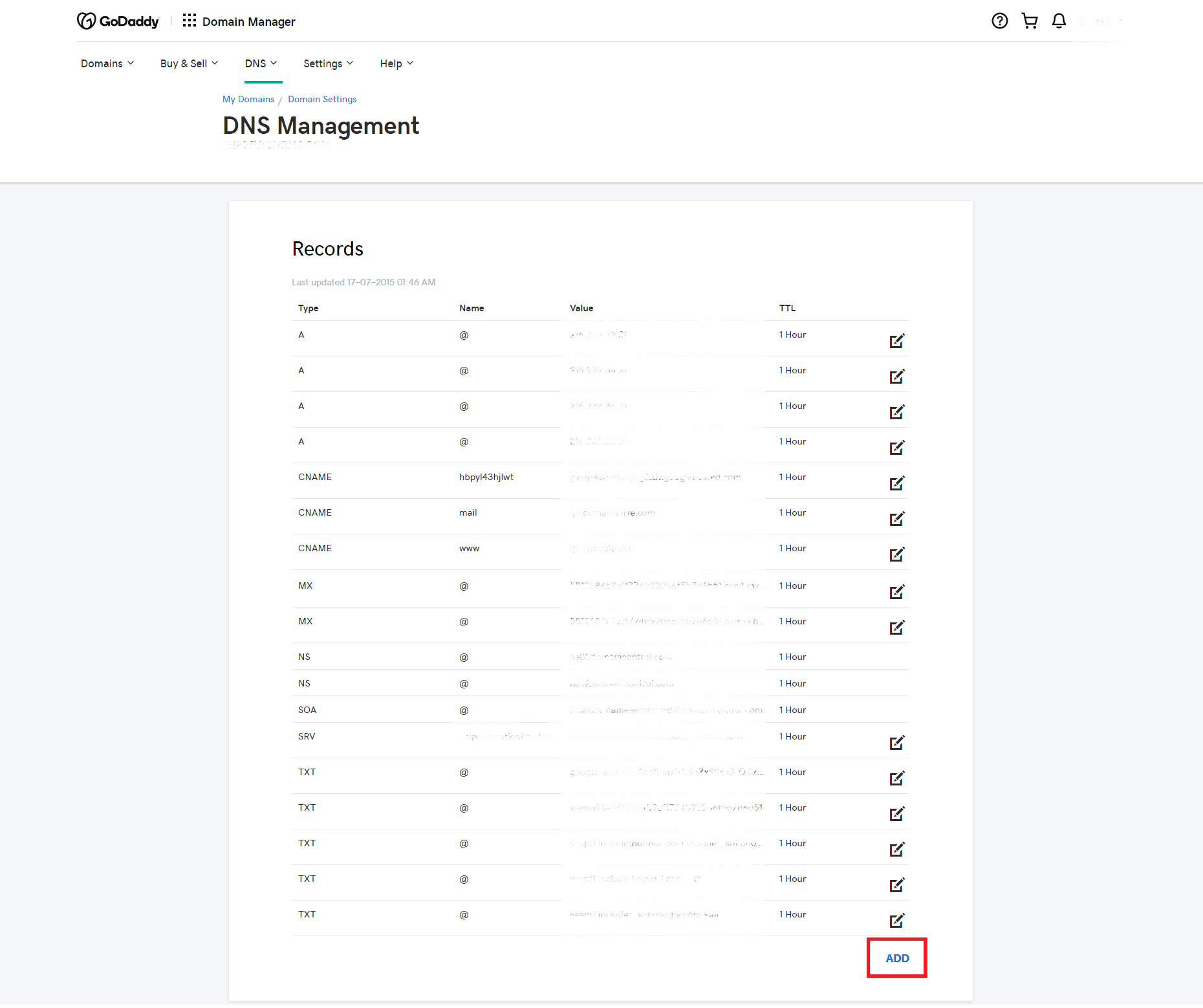
See the image below. Components of a CAA DNS record is explained in the next section.
What Goes into a CAA Record?
Please note that I will only center my discussion on the canonical presentation format of the CAA records for this article as it is stated in RFC 8659, which makes RFC 6844 obsolete.
As you have already seen in the picture above, the CAA record setup is quite nice-looking. It is if you only understand what each part signifies; otherwise, it can be quite bewildering. Let us now look at the components of a DNS CAA record.
Flags
The flag points out whether a record is critical or non-critical. It is denoted by a 1 for critical and 0 for non-critical, as outlined in RFC 6844. 0 is usually the default. However, a Certificate Authority can always create its flag and give specific instructions concerning the certificate’s issuance. The flag denoted by 1 communicates to the Certificate Authority that unless the CA has a clear understanding of the property, it will not be allowed to use the CAA DNS records in the zone. To be more precise, the Certificate Authority will not issue a certificate to the domain. It should notify the domain holder of the failure of the CAA record check through email.
The flag denoted by 0 means that the Certificate Authority is at liberty to use the recorded information in the zone regardless of whether it has a clear understanding of the property. If the Certificate Authority fails to understand the property, the CA can skip over it and look for another in the DNS zone file.
Tags
Tags are the second element of the CAA record. They are tasked with controlling the issuance of DNS records. There are three tag levels: the issue tag, the issuewild tag, and the iodef tag.
The issue tag authorizes a single certificate authority to issue an SSL certificate, other than Wildcard SSLs, for a particular domain name as well as its subdomains. The issuewild tag will authorize a single Certificate Authority to issue Wildcard SSL certificates only for the domain name and its subdomains. The iodef (incident object description exchange format) tag will provide information about any requests for invalid certificates. This is vital to the domain holder as it gives him the ability to receive a communication (made via mail) about a certificate request that has failed the CAA check. Therefore, the domain holder can stay up to date with any issues related to CAA issues and diagnose the errors that cause failures.
Value
Value, which usually appears between two parentheses, refers to the Certificate Authority domain, which has been mandated to issue SSL certificates for a domain.
In any case, the value is a semi-colon, then it means that no certificate Authority has the authority to issue certificates for the domain.
TTL
The final element of a CAA record is the TTL. TTL stands for Time to Live. It’s the amount of time in seconds, which a server should keep your CAA records in its cache.
That looks a lot to comprehend in one sitting. Just take in a deep breath and grab a cup of coffee because there is more to come. Good. Now let us pull all this together.
Examples of DNS CAA Records
For instance, assume that we want a CAA DNS record for yourdomain.com. If yourdomain.com specifies that only Geotrust and Thawte can issue the non-wildcard SSL certificates to it, then the CAA record will look like this:
yourdomain.com CAA 0 issue “Geotrust.com”
yourdomain.com CAA 0 issue “Thawte.com”
Now, assuming that yourdomain.com decides to let only Thawte issue wildcard SSL certificates while Geotrust issues the non-wildcard SSL certificates, then the CAA record will appear as shown below.
yourdomain.com CAA 0 issue “geotrust.com”
yourdomain.com CAA 0 issuewild “thawte.com”
When a domain holder wants to set IODEF properties for his/her CAA records, the arrangement will appear like this.
yourdomain.com CAA 0 issue “geotrust.com”
yourdomain.com CAA 0 iodef “mailto:email@yourdomain.com”
yourdomain.com CAA 0 iodef “http://iodef.yourdomain.com”
How to Add, Edit, or Create A CAA Record?
As a domain owner, you have several approaches at your disposal which you can use to create, edit or add a CAA for your domain or subdomain.
You can use your control panel or the DNS of your domain registrar. We have compiled the procedure for using the control panel and domain name registrar.
How to Add A CAA Record in Domain Name Registrar?
This is basic method of adding CAA Record. This method depends on domain provider and can vary according to domain registrar. Below steps of “adding CAA record” will give you more understanding to add a CAA record in Godaddy.
1. Log in to GoDaddy Domain Control Center.
2. Select your domain to go to the Domain Settings page.
3. In Additional Settings, Choose Manage DNS.
4. Select Add at the end of the record table as shown in the image.
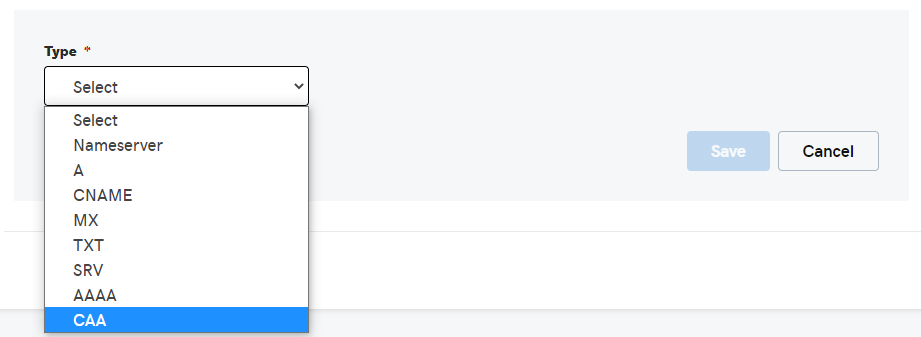
5. Click on Type and select CAA.
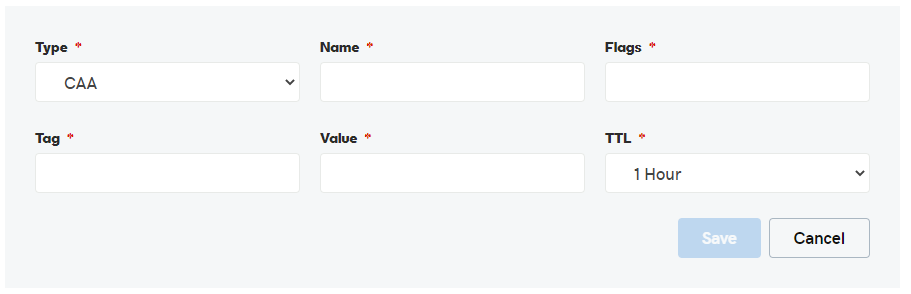
6. Now enter your CAA record details, Name, Flags, Tag, Value, TTL and save it.
How to Add A CAA Record in the Hosting Control Panel?
There are so many types of Hosting Control Panel and cPanel is one of them. Below steps regarding “added CAA record” will give you more insight to add a CAA record in cPanel.
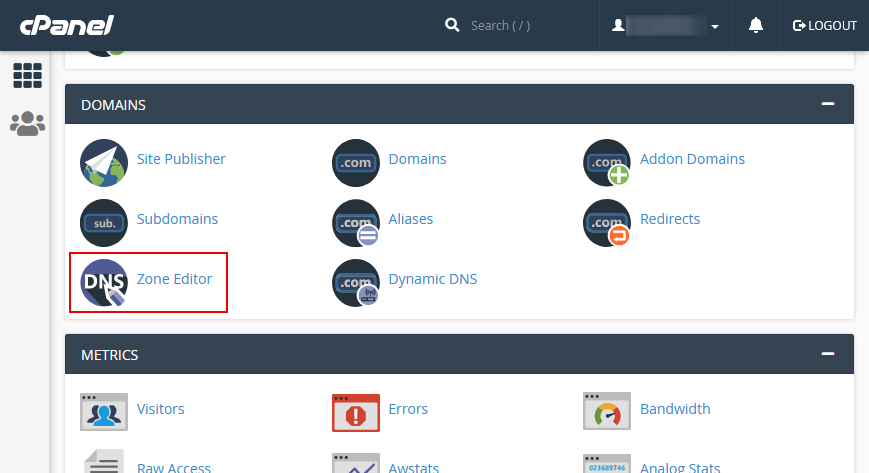
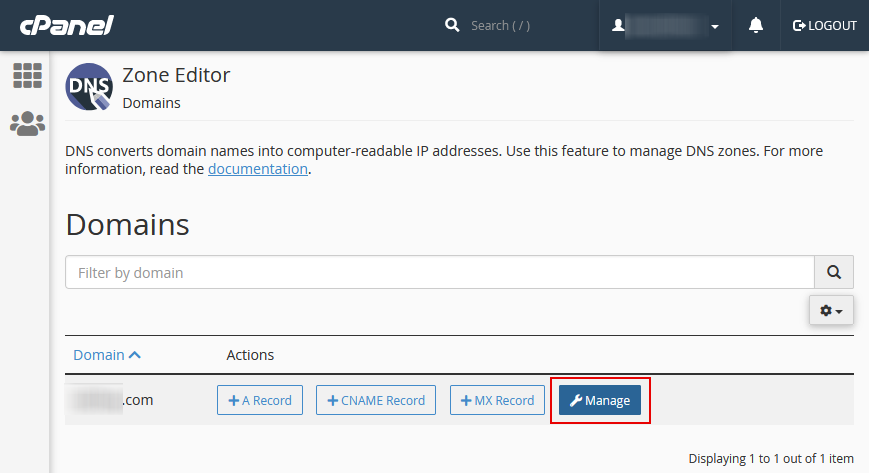
First, you will have to log into your cPanel account. It would help if you then navigate to the “Domains” section and then click on the “Zone Editor” tab. See the picture below:
After clicking on the Zone editor, you will have to find the domain name you wish to add a CAA record. After identifying the domain, you should then click on the “Manage” tab. See the photo below.
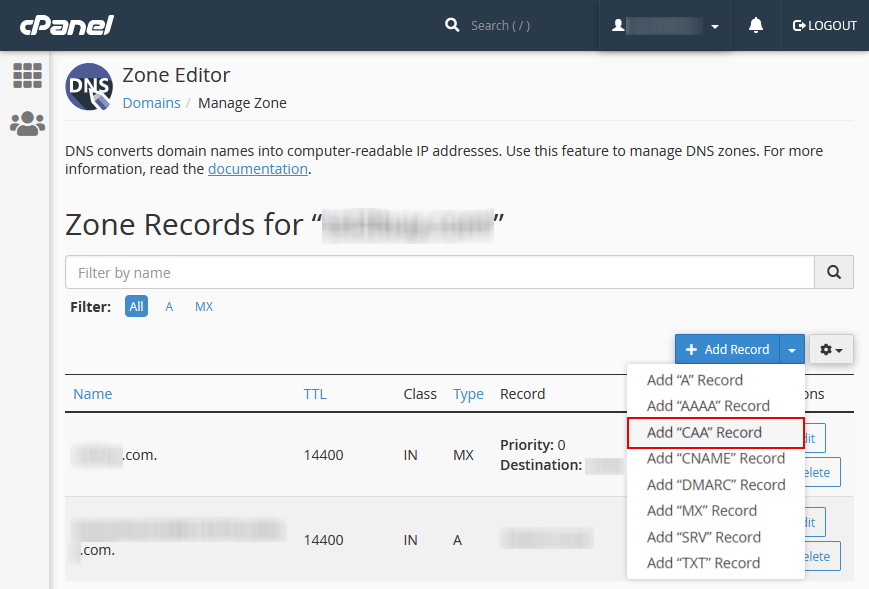
In the zone editor tab, locate the blue-button written off as “Add Record.” A drop list appears. Find and select the “Add CAA Record” tab. See the image below.
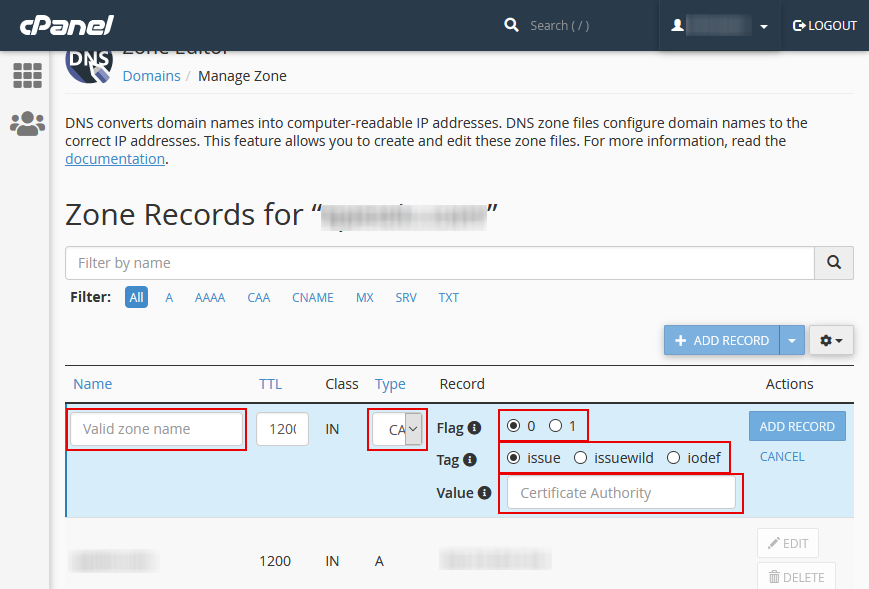
A zone editor menu will appear for that particular domain that you have selected. You will need to fill in the missing details that include the following:
- The name of the website.
- The domain and subdomains for which you want to add a CAA record.
- The flag.
- The tag.
- The value.
After appropriately filling these records, you should click on the “Add Record” tab, which is located on the right-hand side; in so doing, you will be able to save the updates.
How CAA Works and The Role Certificate Authority Authorization Plays in Certificate Issuance
The CA/B forum, in one of its ruling, requires all commercial CAs to check the CAA records before going ahead to issue an SSL certificate to a particular domain. So, when a CA is requested to issue an SSL certificate, the first thing it will do is check whether there exist any CAA records for the domain in question.
In the presence of a CAA record, the Certificate Authority will have to check and determine if they are accredited to issue SSL certificates for the domain. Furthermore, the CA will need to go through the CAA record specifications to decide whether it matches these specifications. If the CA meets all these thresholds, then it can go ahead and issue the certificate. If the CA fails to meet any of these specifications, then the Certificate Authority should reject the request. In the absence of a CAA DNS record, the certificate authority can proceed to issue the certificate.
Certificate Authority Authorization plays a very crucial role in certificate issuance. It is both a control and security mechanism. If you consider several CAs and only need to pick the most eligible and trusted one, then the Certificate Authority Authorization concept will come in handy. You can dictate which CA is authorized to issue a certificate, and only that CA will be able to do so. Such policies as CAA holds a bigger place in the large organizations where explicit purchase policies have been laid down. Policies might exist which require particular CAs to issue certificates. Honestly, making such communication across multiple departments is not just a walk in the park. Imagine a scenario where a new employee comes in. The employee does not know the policy and easily requests a certificate from the wrong CA. However, in a situation where the organization uses CAA records, then it is easy, even for the newbies, to get certificates from trusted and authorized CAs only.
Why Do You Want to Consider Creating A CAA DNS Record for Your Domain?
The significant advantage of creating a CAA DNS record is to avert the issue of certificate mis-issuance. However, you should note that this is not the only reason for creating a CAA DNS record. Other reasons include the following.
- Creating CAA DNS records helps to safeguard the identity of the domain name holder. Specifying which CA can issue your certificates allows for denying hackers an opportunity to request a certificate from unauthorized CAs.
- Creating CAA DNS records will help you to prevent shadow certificates.
- CAA helps you to show your preference and support to particular Certificate Authorities.
- With Certificate Authority Authorization, it is easier to manage your certificates because you have them under one umbrella. It is easier this way than trying to track certificates from multiple Certificate Authorities.
Conclusion
Although not foolproof, the Certificate Authority Authorization is a relatively cost-effective approach to preventing certificates’ mis-issuance. It will work best with other techniques and tools to safeguard your domain name and website. You have already seen the many advantages that come with creating a CAA DNS record. This article has provided greater clarity on the CAA and why it is so crucial. It also provides a clear procedure on how to create or update your CAA record. It will help you manage your certificates like a boss.