Vulnerability Management Explained – Types, Process, Use Cases, and Best Practices
Cybercriminals can exploit vulnerable areas of your company for their gain. Addressing and managing vulnerabilities is a practice of threat detection and remediation. Some vulnerabilities result in network and software issues and securing them takes time. It means finding and fixing weak spots. Regular updates provide a safer and more secure operating system.
What is Vulnerability?
Vulnerability is risk-prone or weak areas of network or software devices. It can lead to cyber threats. Every organization has some vulnerabilities in most of its systems. Like unencrypted devices, poor storage devices, and passwords. It is important to implement effective security systems to prevent cyberattacks. Implementing a security strategy can help businesses avoid severe damage.
Types of Vulnerabilities
-
Hardware & Software Vulnerabilities
Flaws in devices or systems create hardware vulnerabilities. They permit attackers to exploit the system from a distance or in person. Unencrypted devices, storage, and old system versions are hardware flaws. Hackers target organizations that have high-value data in their systems. Hardware flaws can cause a bad reputation and financial damage.
-
Software Vulnerabilities
Software vulnerabilities are ones where attackers target software and access devices remotely. They occur when there is a flaw in the coding or design of the software. For example, some software vulnerabilities lack input validation, cross-site scripting, etc;. As hardware vulnerability, it can also cause major damage to businesses.
-
Network Vulnerabilities
Network vulnerabilities can cause hardware and software issues. They often result from malware, misconfigured firewalls, and social engineering attacks. Unprotected communication also adds risks. Simple networks usually run many applications and systems. Flaws in these systems can let attackers break network vulnerability.
Filtering and scanning network traffic helps find threats. Regular monitoring allows organizations to spot patterns and block early attacks.
-
Procedural/Operational Vulnerabilities
Organizations often have security flaws. It makes them easy targets. Organizations should use standard password policies to boost security. Also, maintaining proper procedures is vital. It’s crucial to know the best practices to avoid cyberattacks. This helps prevent exploitation. Training and sharing knowledge is the key. This helps prevent malware attacks and exploitation.
-
Operating System Vulnerabilities
Operating system vulnerabilities are flaws in software or code. Hackers exploit OS to access it and damage it. They target logical errors or coding mistakes. These common threats include malware, network intrusion, buffer overflow, and virtualization attacks. It is difficult to detect OS vulnerabilities. Creating error-free software is tough. It’s hard to hack OS because OS’s have complex functions.
What is Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability management is a systematic, strategic process. It identifies, assesses, and manages security vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and software. It also includes remedial measures. It tracks risks and provides security in organizations. Thus, organizations must keep security systems and lower threats to prevent data breaches.
Need for Vulnerability Management
Vulnerabilities are gaps that cybercriminals exploit. As these gaps grow, the need for cybersecurity becomes crucial. Vulnerability management identifies and assesses IT system risks. Also, it removes or fixes them.
Here are points that explain the importance of vulnerability management:
- Vulnerability management aims to scan, investigate, analyze, and report risks or security flaws. It also seeks to reduce them. This process is ongoing and crucial for preventing cyberattacks.
- It identifies weak points to secure the network. It’s key to good cybersecurity and can improve security systems.
- Vulnerability scanning is vital in the initial phase. It tests for vulnerabilities detects them and evaluates them. Finding these weaknesses prevents further damage. NIST recommends scans every quarter. For high-traffic or sensitive data organizations, monthly scans are advised.
- Network and computer security are crucial in this process. They tackle information security risks and fight cybercrime. This approach provides a constant view of IT risks.
- Many tools are available for scanning and detecting issues. They enhance the process more than manual methods. Though these tools require an investment, they are worth it. They save money and protect sensitive data.
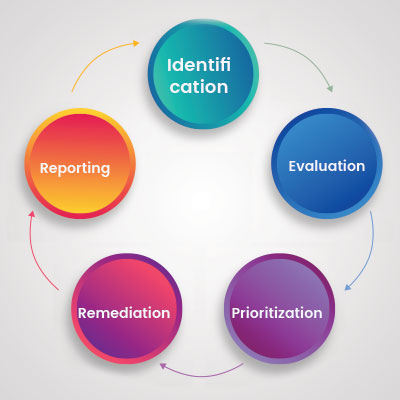
Five Stages of the Vulnerability Management Process
Identification
Identifying vulnerabilities is the first step in locating the gaps and bringing insights. Vulnerability scanners work step-by-step on the network systems. They identify and gather all the system information. You scan it periodically to find misconfigurations and reduce risks. It is also essential to check the reports and results from the scan. Verify any vulnerabilities or risks found in the system.
Evaluation
After spotting vulnerabilities and details, the team creates a report. They rank vulnerabilities by their scores. They use the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) for this. Different tools assess various vulnerabilities. Web app scanners look for known attack patterns. Protocol scanners check active IP protocols. Port scanners find open ports. Network scanners search for suspicious signals, IPs, and operating systems.
Prioritization
The growing vulnerabilities make it hard, and sometimes impossible, for organizations to fix each one. Remediating vulnerabilities is better if we prioritize them by risk. It further analyzes the metrics and ratings from the scans and discovery reports.
Treating
This step is the next one to treat the gaps of vulnerabilities identified. The right remediation approach and specific treatment strategies are crucial in this process. The primary purpose of this step is to treat all the security gaps and vulnerabilities. An organization must plan steps for effective fixes and prevention. Key steps include adopting new tools, enhancing security, and regularly updating operations.
Reporting
This step is vital for sharing the summary and findings about asset security gaps and risks. It also offers insights into the main vulnerability and how to fix it. Key parts of a vulnerability report include an executive summary, an assessment overview, and details on each vulnerability.
The executive summary gives details of issues and risks and prioritizes them accordingly. It also includes details on findings, primary objectives, and remediation of all details. Like names and times of servers.
The assessment overview helps the program owner understand scans. It includes details on validation, investigation, and deliverables. Individual vulnerability details cover the name, discovery date, score, proof of concept, impact, and treatment guidance. This section ranks vulnerabilities by severity, listing higher-risk problems first.
The 5 Essential Steps to Improve the Vulnerability Management Process
- First comes the scanning process. It requires all the resources and systems for scanning. It also compiles and configures all the parameters needed for the scan.
- The next step is to scan for vulnerabilities. This would use all resources and systems to report on their cybersecurity features.
- After analyzing the data and finding vulnerabilities, a remediation plan is next.
- Implement the remediation plan in the best possible way for maximum results.
- A follow-up scan ensures and assesses the plan’s success. This leads to its implementation.
Practical Steps to Build a Threat and Vulnerability Management Program
To build a threat and vulnerability management program, follow these steps:
- Regular testing for penetration.
- Maintain a patching schedule.
- Track all IT assets and networks.
- Stay updated on current threat intelligence.
- Weak cybersecurity infrastructure
- Service Level Agreements and remediation clauses.
Regular Testing for Penetration
Network security is a priority for cybersecurity against external attacks. Penetration testing is also known as pen testing. It is effective in network security threat management. It benefits businesses by detecting and fixing vulnerabilities and securing a network.
Maintain Patching Schedule
Frequent software updates are necessary as there is always scope for improvement. Regular updates make every software secure. Along with updates, consistent systems and software patching work best for secure networks. It’s always a good practice to test an update before applying it. This helps avoid issues after each update.
Track all IT assets and networks
As the software works on vulnerabilities, the hardware needs attention. An old or forgotten piece of hardware or program could be an easy target for hackers to exploit. In addition, missing or forgotten hardware can be an expensive vulnerability. So it’s essential to keep track of all your software and hardware assets regularly.
Stay updated on current threat intelligence
Information is always less when it comes to growing cyber threats. It is always the best choice to stay updated on threats and vulnerabilities. Following and tracking potential vulnerabilities keeps your network safe and helps avoid threats.
The sooner we find the vulnerabilities, the faster we can fix them. Vulnerability assessment and threat intelligence tools maintain security for your network system.
Weak Cybersecurity Infrastructure
An organization needs to maintain good cybersecurity practices for a safer infrastructure. The employees and staff should properly understand cybersecurity practices and manage them. Any negligence or bad practices can lead to exploitation. So, regular updates and training are needed to maintain good cybersecurity.
Service Level Agreements and Remediation Clauses
When third parties are involved, it needs an agreement to set deadlines for fixing vulnerabilities. Unpatched vulnerabilities remain a threat for a longer period. So, Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with favorable terms are vital for network protection.
Vulnerability Management vs. Vulnerability Assessment
| Vulnerability Management | Vulnerability Assessment |
|---|---|
| It is a continuous process and comprehensive program to manage and mitigate cybersecurity vulnerabilities. | It has a timeline with start and end dates that can also be called a one-time project. |
| It’s a step-by-step process and well-planned practice in organizations for managing risks. | It improves IT cybersecurity and plays a vital role in vulnerability management. |
| It has four steps Asset inventory, Information management, Risk assessment, Vulnerability assessment. | its part of vulnerability management and is one of the crucial steps of it, which plays a vital role. |
| It asset inventory information related to cybersecurity and understands threats with risk management. | It determines the threats and helps mitigate risk and strengthens cybersecurity. |
Practical Implementation of Vulnerability Management
After completing the steps in vulnerability management, we must implement them. A systematic and correct approach is crucial. Here’s how to do it:
Identify and define your goals
The primary purpose of vulnerability management is to identify and mitigate security risks. However, the other objectives are implementation and overall vulnerability management improvement. These objectives include periodic scans and any tools to find open ports.
Roles and Responsibilities
As per your organizational structure, every individual should follow their roles and responsibilities. Security practices for staff help build a robust security system. Monitoring and assessing risk with each alert mitigate any future risks. Resolvers locate the known issues and work on patches or solutions. Cybersecurity experts work on strategies and procedures to reduce vulnerabilities. They also work on how to be ready for future attacks.
Assessment of the Vulnerability Management Program
Vulnerability management updates you about the security status of your organization. But a regular assessment gives you a clear idea of the areas for improvement for good results. The change in technology makes regular scans a priority for vulnerability solutions. It also provides a real-time view.
Importance of Vulnerability Management Tools
The need for cybersecurity rises with the increase in cyber threats and vulnerabilities. Organizations should implement tools to reduce and manage risk periodically. If the tool detects a major vulnerability, it needs immediate action. Vulnerability Management tools have two main sections that inform their functionality. The first one deals with the threats and risks that a business might face. The other is mitigating risks and threats.
Business Cases for Vulnerability Management Tools
The vulnerabilities in the IT sector are impacting different organizations in different ways. Therefore, we can understand the need and value of vulnerability management tools. Here are some of the cases below:
Small Businesses
Small organizations often struggle to budget for security and staff. Additionally, employees find it hard to gauge the impact of potential vulnerabilities. However, simple tools or scanning services can help. They make it easy and affordable to check for vulnerabilities regularly, provide detailed reports, and enable timely fixes.
Medium-sized Businesses
Medium-sized businesses also face the same problem as small businesses. However, they have higher chances of facing more losses. With the increasing threats, the chances of targeted attacks are also increasing. It requires skills and staff to manage proactive security. Given all these factors, like cost and skills, using tools is better. We need experienced staff to manage data security. A limited budget and effort are not worth the investment.
Enterprise Organizations
Large companies are prime targets for cybercriminals. They have vast data and many network points. So, they need to manage their data and security effectively. A strong tool is essential for assessment, scanning, and reporting. Also, laws, audits, and policies demand a vulnerability management plan to manage risks and stay compliant.
Risk-based Vulnerability Management
Risk-based vulnerability management is one of the most popular vulnerability management strategies. It depends on the level of risk it may pose to an organization’s network and digital assets.
The following are three main factors that help identify the prioritization of the vulnerabilities based on risk.
- Core Business Risk: Every business must identify important processes and digital tools. These are essential for day-to-day operations. Once a weakness is found, it is given priority based on how it could impact the digital tools. This factor has the biggest effect on risk priority. It is directly linked to the business’s reputation and income.
- The extent of Exposure: Risk scores associated with a vulnerability also determine the volume of digital assets exposed. The risk score is directly proportional to the extent of exposure.
- Preparedness: This factor addresses organizational readiness against identified vulnerabilities. It also analyzes whether the organization has defined standard operating procedures or solutions. Also, verify possible exploitations of identified vulnerabilities. If the preparedness level is high, then the risk will be low. However, an organization should consider adding more security measures to protect digital assets. Imply vulnerability management if there is no resolution set for the identified vulnerability.
The Need for Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
An organization with a large scale of data is challenging to manage for cybersecurity teams. On average, 80,000 IT assets are managed by the cybersecurity team. Like laptops, printers, routers, etc. As per research by Kenna, out of every 10 vulnerabilities, you should at least resolve one. They also said even a small change can make a huge impact on your organization. It all says that risk-based vulnerability management is necessary. The vulnerabilities are prioritized as per regulatory, compliance, or other needs. Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is one standard metric used to score vulnerabilities. It marks as per risk or damage expected from successful attacks.
Three Important Rules to Follow in Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
- Vulnerability Scanning
Scanning works on identifying and determining the security strategy. The risk-based vulnerability management approach detects and guides the remediation of vulnerabilities. It works according to the highest priority based on the threat surface of the vulnerabilities. - Remediation
Remediation is the key, as regular alerts are generated for continuous scanning. The alerts enable the remediation or fixing of the vulnerability faster. - Prioritization
In a risk-based management system, the vulnerabilities are prioritized according to risk. The risk prioritization program determines the highest-risk patches and focuses on patching them. The risk prioritization gives a clear understanding of exposure and vulnerability severity. It also gives a clear idea of the application of the remediation techniques.
Different Businesses with Common Vulnerabilities
There are specific businesses that are the most targeted for their vulnerabilities. Weak businesses are easy targets to break and steal valuables. All kinds of organizations are at risk. Most sensitive and attractive targets are health care, Banking, and Educational Institutions.
According to DBIR (Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report). Out of 819 incidents, 228 were in Educational Institutions.
2020 is recorded as a hike in cyber attacks due to weak firewalls, cybersecurity systems, and recovery plans.
Cloud servers also grew with VPN usage in 2020. Cloud-based vulnerabilities are like a failure in configuring Office 365 security settings.
Compared to other sectors, educational sectors have poor reporting time, and more phishing attacks.
Around 92 cases of data disclosure in food services and 25 in Construction industries.
Lack of employee training for malware and cybersecurity leads to vulnerabilities and threats.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are exposed to the internet and highly vulnerable as it is often left unpatched.
Ransomware attackers exploit VPNs using arbitrary code execution or file reading vulnerability.
Widely used and popular software in companies is also targeted by hackers.
For example, Adobe Flash Player was impacted by UAF (Use After Free) vulnerability which was a memory corruption bug.
Additionally, Microsoft Office Memory Corruption Vulnerability impacts MS Office. It allows attackers to install malware or run malicious commands and other issues that need regular patching.
Vulnerability Management Best Practices
Define a vulnerability management strategy
Vulnerability Management is a continuous process. It depends on some crucial factors to succeed in an organization. One of the crucial factors for successful Vulnerability Management is a well-planned strategy. A strategic plan organizes and combines people, technology, and processes to work effectively. It also saves organizations from cyberattacks and security risks.
Maintain Vulnerability Database
A Vulnerability Management Database shows all of a business’s IT assets. Such as applications, infrastructure, devices, databases, content systems, and servers. It’s crucial to update it regularly. This ensures better visibility into your assets, systems, and processes.
Automate
Organizations should automate scanning and event-based response systems. It makes the organization agile in handling threats better. Various tools help to identify or scan vulnerabilities regularly. These tools automate the process of vulnerability management by scanning and generating reports. Which gives a clear idea of the security threat.
Incident Response Plan
The processes involved in vulnerability management are sustained and repeated for effective implementation. For any kind of security breach, there should be a plan of action in organizations. On the verge of a security breach, a response plan saves time and acts quickly. It mitigates risk and safeguards digital assets.
Training
Skillset is very important in vulnerability management. Employees with good cybersecurity knowledge are good for the vulnerability management process. Regular training for vulnerability dwell time, qualitative metrics is also important.
Vulnerabilities Management Continuous Approach
Effective vulnerability management comes with a continuous and organized practice. Organizations need yearly planning and practice rather than once or twice a year. Companies should avoid “vulnerability debt” to prevent cyberattacks and network susceptibility. Vulnerability debt can be referred to as the cumulative cost of neglecting vulnerabilities. These are the known non-critical vulnerabilities that are ignored or accepted temporarily. Although it is critical to maintain effective vulnerability management. Try to do regular practices, assets, and alterations in scan, or reporting.
Vulnerability Debt
Vulnerability debt can be referred to as the cumulative cost of neglecting vulnerabilities. The vulnerabilities considered non-critical, ignored, or left untreated eventually impact financially. It becomes difficult to secure data from cyberattacks cause of the long-term accumulation in software.
As the older version remains untreated, the new ones are also detected. It increases the effort to secure the system. Even after the decision to upgrade is made, challenges do exist. As the software evolves and advances with time, temporary vulnerabilities become complicated. Sometimes the vulnerabilities considered non-critical prevent the healthy development of a system. Vulnerability debt not only stops with financial loss. It also includes litigations, loss of brand equity, regulatory penalties, and more. Therefore, keeping weaknesses away and avoiding vulnerability debt is a good decision.
Conclusion
The cyber world will always face threats, and vulnerabilities are part of them. Vulnerability management is the best decision for identifying vulnerabilities and to prevent them. It provides an organized approach to managing cybersecurity systems. It also mitigates risks and applies safer cyber environments.