The Internet is experiencing a new wave of virtual experience, named Metaverse. As the internet grows, users are getting more interested in immersive experiences in terms of gaming, shopping, and buying virtual assets.
The Metaverse lets millions of people build new interactions and digitally recreate ones that are more like the real world.
According to recent statistics, the Metaverse market is expected to reach $74.4 billion by 2024. Thus, businesses can get good opportunities from such booming interest, by introducing an immersive environment and creating avatars.
From a business perspective, the Metaverse opens up new ways to grow, improves ties with customers, and changes how costs are calculated. More and more growth possibilities will show up as digital interactions become more immersive and relevant.
But from the cybersecurity point of view, this trend brings up big challenges that businesses need to consider.
As the Internet grows, cybercriminals have more places to hit. As these experiences become more realistic, users worry about their safety and security even more. This is because what they see, hear, and feel is becoming more like real life.
Cybersecurity is one of the most crucial elements in the Metaverse. By working to bring Metaverse projects to market, cybersecurity companies help keep customers safe and protect the investments their companies have made. Cybersecurity is very important for building the trust needed to take advantage of these new possibilities.
This blog addresses top Metaverse cybersecurity challenges and how to solve them to deliver secure virtual experiences.
Understanding The Metaverse Concept
The Metaverse is a futuristic concept that is now thriving in the digital landscape, where reality and imagination co-exist to deliver an immersive user experience.
With each passing day, the Metaverse is innovating, expanding, and evolving an unprecedented amount of opportunity for playing, socializing, working, and exploring creativity. It enables businesses to create digital assets that people can buy and sell, inspiring a new trading concept.
Now let’s learn how it works and the supporting technologies that make it a reality.
How Does The Metaverse Work?
In Metaverse, the users can create their 3D avatars to experience the virtual world. They can experience immersive games, shopping by trying out products virtually, trading, chatting and much more. It’s like your digital avatar in a digital landscape. It works on these innovative technologies:
Technologies Of Metaverse
Virtual Reality
It is the most common technology and most of the gaming and real estate concepts can be designed based on it.
Augmented Reality
This technology works perfectly for creating virtual shopping experience platforms.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is crucial in the Metaverse, as it tracks users’ motions, senses their actions and identifies retinal movements.
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing helps implement AI-collected data to deliver personalized virtual experiences.
Internet of Things
IoT is crucial as an immersive experience cannot be possible by using VR headsets, sensors, and mobile devices. Meta Quest and its competitor Apple Vision Pro are the best examples of IoT in the Metaverse.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is useful for storing user’s Metaverse data, its avatar and other important information to deliver end-to-end user experience without any hassle.
Blockchain
It is necessary to process data, make payments and other important stuff in the Metaverse landscape.
High-End Sensors
Sensors are the crucial elements in eliminating the difference between the real and the virtual world.
3D Graphics
Lastly the entire experience is useless if there is no high-definition 3D graphics that cater to the user’s fantasy and virtual lifestyle.
Businesses can leverage the expertise of software developers, blockchain developers, graphic designers, and prompt engineers to create unique Metaverse platforms for their targeted audience.
However, Metaverse is an emerging technology and is vulnerable to a multitude of new cyber threats and malware.
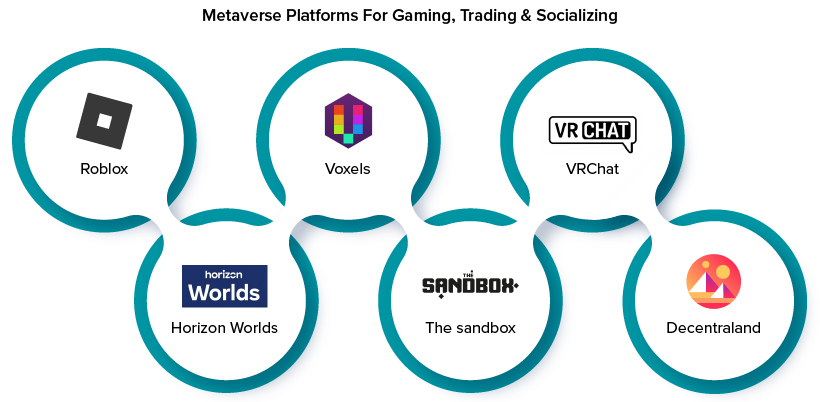
Top trending Metaverse platforms for gaming, trading and socializing
Roblox
One of the massive gaming platforms, Roblox is home to a number of Metaverse experiences that include, fashion shows, music concerts, building blocks, martial arts and educational classes.
Voxels (formerly Cryptovoxels)
Powered by Ethereum blockchain, Voxels enable users to create their own digital assets, lands and NFTs that they can trade virtually.
Horizon Worlds
Top brands like Nike and Adidas have invested in this Metaverse platform, helping consumers to try out their products virtually and enhancing the sales possibilities.
The Sandbox
Designed to trade in virtual land, Sandbox is focused on building a community where players can vote and earn rewards based on their voting.
VRChat
As the name itself suggests, it enables users to socialize and communicate with each other using their 3D avatars.
Decentraland
Decentraland is the first-ever virtual world or platform created and owned by its users. This means no one controls the platform or decides its future. It is an open-source platform which allows anyone to make improvements or build on it.
Thus, these are the diverse examples of Metaverse and how they are impacting the digital user experience.
Top Metaverse Cybersecurity Challenges
The Metaverse is the new advancement that the world has seen so far and has the potential to create new opportunities in new markets and industries. However, with new advancements and innovations, the Metaverse comes with its own security challenges. Security risks in any sort of digital environment already exist in the form of phishing, scams, impersonation, and credential theft. Let’s have a look at some Metaverse cybersecurity challenges.
Privacy
For users, the biggest concern about the Metaverse idea is probably the safety of their data. Statista reports that “tracking and misuse of personal data” has been named as the biggest worry of US Internet users about the Metaverse. Over half of the people who answered said it was a major worry, and another 24% said it was a minor concern. The number of people who don’t think their privacy might be invaded in Metaverse is now 21%.
Privacy is a big issue for most people who use the Internet these days. A big issue has come up because of the pressure, and society has changed because of it. People don’t want third-party cookies anymore, so it makes sense that people won’t want to track and sell data in the Metaverse either.
Identity Issue
Identity and identification become crucial considerations in the Metaverse as users create virtual avatars. These avatars can mimic realistic individual features, posing several security challenges. Account hacking and unauthorized avatar takeovers pose substantial hazards to the integrity of user interactions in the virtual realm.
Furthermore, many unverifiable identities complicate authentication processes, raising the risk of fraudulent identities being used for harmful purposes. The lack of a centralized authority complicates the management of virtual identities, necessitating novel ways to assure the validity and security of user interactions.
Cyberbullying
As the Metaverse creates a dynamic environment where users can create and exchange material, moderating issues arise in managing the huge and diverse virtual terrain. Ensuring the safety and appropriateness of supplied content is a challenging endeavor.
Cyberbullying in the Metaverse necessitates robust content control techniques. The decentralized nature of the Metaverse complicates matters further. Standard moderation systems need help to keep up with the massive amount and diversity of information produced in this digital environment.
Device Vulnerabilities
The most important challenge in safeguarding the Metaverse is the vulnerability of the devices. Devices like Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality sometimes need users to enter personal information. This situation allows possible entry points for cyber-attacks.
These can result in illegal access, data breaches, and even the compromise of virtual identities. Metaverse devices are vulnerable to hacking, malware, and cyberattacks. It necessitates strong security measures to protect user data and maintain a secure virtual environment.
Decentralization
Decentralization is a key principle of the Metaverse and it poses new cybersecurity challenges. Unlike typical internet platforms, the Metaverse lacks a centralized authority, making it difficult to create uniform standards for security and administration.
This fragmented structure creates challenges, such as a lack of defined regulatory frameworks, making it difficult to apply cybersecurity measures consistently. Decentralization further increases the complexity of responding to cyber threats because there is no centralized institution to coordinate and implement security policies across Metaverse.
Data Theft
Metaverse houses an enormous quantity of confidential information and IP addresses. Everyone from governments and regulators to regular internet users is increasingly concerned about data privacy. Increasing data exchange and exposure with digital enterprises is necessary for the creation of avatars that can “live” and “co-exist” in the Metaverse and engage in activities there.
Some worry that connecting to the Metaverse would lead to more tracking and evaluation of their online activity, with the eventual sale of this data to advertising. The risk of private information theft grows in proportion to the amount of personal data that people post to the Metaverse.
More sensors in homes and businesses will likely be required for the Metaverse to reach its maximum potential. The useful capability of these gadgets to track user activities and behaviour in real-time makes them more susceptible to targeted cyber-attacks.
What Hackers Target In Metaverse?
Metaverse hackers typically target NFTs, cryptocurrency wallets, and other valuable assets within the Metaverse. Also, some hackers may create and spread malware or engage in phishing scams within the Metaverse. Here are some of the Metaverse hackers targets:
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs are unique digital assets in the Metaverse. These unique tokens are stored on blockchain networks, making them a tempting target for hackers. One typical method is to create NFTs or exploit flaws in smart contracts.
It results in unlawful transfers or sales. In some cases, unknowing consumers fall victim to acquiring counterfeit or stolen NFTs, resulting in money losses and compromised virtual ownership.
Cryptocurrency Wallets
These crypto wallets have become a popular target for hackers. It holds different types of digital currencies that are used for transactions, investments, and virtual asset ownership.
Hackers use a variety of tactics to benefit unauthorized entry to virtual wallets. Once hacked, hackers can drain cash, manage transactions, or lock customers out in their bills. It results in substantial financial losses for individuals and businesses operating in the Metaverse.
User Accounts
Metaverse hackers used to spy on user accounts in the platforms, as these accounts have identities that can be stolen or sold on the dark web for financial gain. These accounts basically hold information like passwords which can be used to attempt privacy breaches.
Metaverse Security – Best Practices To Prevent Metaverse Crime
It is important to address Metaverse cybersecurity challenges and it requires a strong approach which is multifaceted. Here, we are going to have a look at some of the best practices that you can take to get prevention from Metaverse crime.
-
Implement Multi-Factor authentication (MFA)
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication for your accounts improves your Metaverse security. MFA adds extra security by needing your password and a temporary code from another device, such as your phone. This makes it far more difficult for hackers to obtain illegal access because they require your password and physical possession of the other device.
-
Opt For a Single Sign-on
Single Sign-on enables the users to access all the resources on one single device without any credentials. It is designed to streamline the login process most securely. It works independently of the password management tool and is often combined with multi-factor authentication.
-
Decentralized Security Protocols
Implementing decentralized protection protocols, which include blockchain generation, can help to secure the Metaverse. Blockchain’s transparency, immutability, and decentralization make it an effective opportunity for shielding transactions and virtual property.
-
AI-Powered Threat Detection
Implementing artificial intelligence for actual time chance tracking and analysis can discover anomalous styles or behaviors. It takes into account the timely mitigation of cyber dangers. The Metaverse’s dynamic environment enables AI structures to adapt to evolving cyber threats.
-
End-to-End Encryption
E2EE for communication within the Metaverse ensures that sensitive data is protected and confidential. This prevents illegal data interception while also protecting user chats and transactions. Explore how businesses can add an extra security layer to their privacy and make secure communication by integrating E2EE technology.
-
Regular Security Audits and Updates
Conducting regular security audits and keeping software and systems updated are essential practices. This enables identifying and patching vulnerabilities, lowering the threat of exploitation via cybercriminals.
Conclusion
Metaverse may look promising, but it includes several hazards and cyber risks that cannot be ignored. Businesses must need to create a secure Metaverse eco-system for their users to safeguard them from phishing, data theft and other types of cyberattacks.
Single sign-on, multi-factor authentication and decentralized structure can be taken as the best security measures to protect the Metaverse platforms from malware and illegal activities.
Thus, the Metaverse’s future depends on increasing security measures that ensure a safe and thriving digital environment for users to explore, interact, and innovate.