Understanding The Role of Cyberspace in Evolving Technologies and Cybersecurity
Cyberspace is filled with data that has become an asset in this digital era. Many crucial infrastructures such as healthcare, financial services, and power plants use the internet for data storage and communication. So, it becomes indispensable to secure the data to prevent cyber-attacks from hackers. The cyber-attack will cost millions of dollars, loss of data, reputation damage, and distrust among the consumers. To avoid such scenarios, cyber security should be given more importance. This document covers various topics such as evolving technologies in cyberspace, cybersecurity trends, the future of cybersecurity, etc.
What is the Cyberspace?
Cyberspace is defined as a virtual and dynamic environment comprised of electronics and communication devices over various networks to store and utilize electronic data. The cyberspace structure is like the structure of a human brain. A human brain consists of a gazillion neurons used to send signals; likewise, cyberspace consists of numerous network connections to communicate. The primary purpose of creating cyberspace is to share information and communicate across the globe. But now the cyberspace is serving beyond its initial motive. It plays an important role in our day-to-day life. Cyberspace network devices include personal computers and servers, supercomputers and grids, sensors, and transducers, etc.
Evolving Technologies in Cyber Space
Various technologies are evolving in a cyberspace communication network. They are as follows.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The concept of AI is to imitate the problem-solving and decision-making abilities of the human brain. It involves creating intelligent computers using advanced programs. The AI works on two basic ideas: thinking rationally and acting rationally. The former deals with thought processes and reasoning, while the latter deals with behaviour.
For example, if we provide a thousand photos of trees to the computer, it scans and stores the data, which can be used to identify the trees. There are two types of Artificial Intelligence.- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI): The computer is trained to pivot on a specific task. It can perform a particular task with a great speed and accuracy that no human can do. It is used in various applications such as Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, autonomous machines, etc.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): Here, the computer will have general intelligence like humans. It works based on self-awareness which is used to solve problems, learn from the past, and plan. This type of AI is purely theoretical and does not have any practical application.
-
Machine Learning
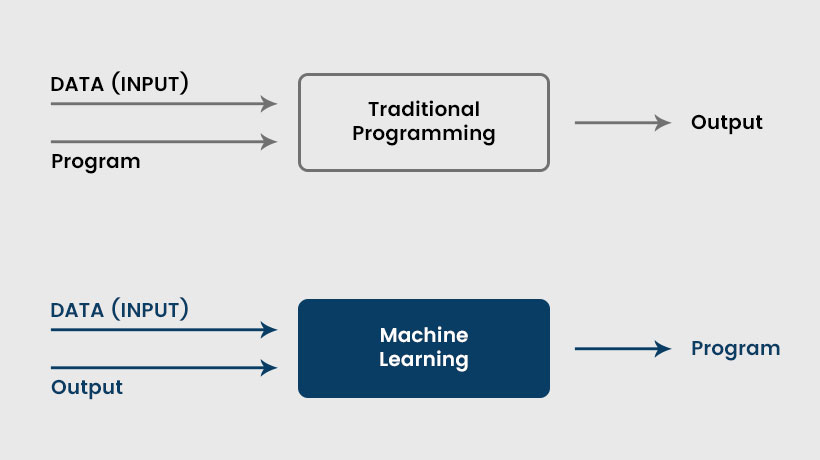
It is one of the sub-fields of Artificial Intelligence that works on the concept of self-learning. Instead of programming the computer to do its task, the computer is allowed to learn from the available data in machine learning. This is also known as the bottom-up approach.
Machine learning involves programming computers to access the data and use it for self-learning. The computers look for data patterns to make decisions by themselves. There is the various real-time application of machine learning, such as- Traffic alert- Google maps
- Transportation and communication- Ola, Uber.
- Product recommendations- Amazon, e-bay.
- online video streaming- Netflix, Prime.
-
Internet of Things
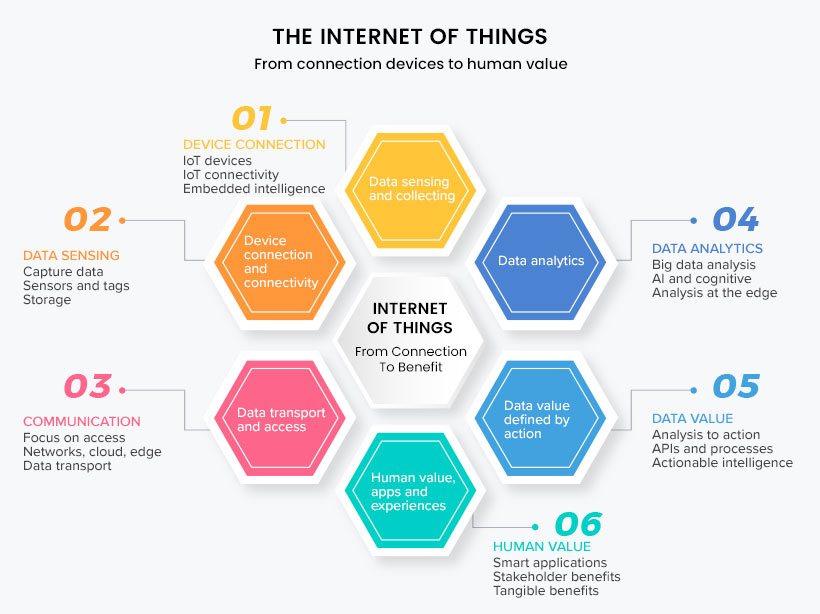
As the name suggests, the Internet of Things refers to a fabricated network of physical devices worldwide connected through the internet. Any device implanted with appropriate sensors, software, and technologies can relate to other devices over the internet to send and receive data without human intervention. The use of IoT is endless, from household devices to industrial machines. It means that any device connected over the internet becomes a part of IoT.
Once the devices are connected to an IoT network, they can be operated from any part of the world without physical contact. It uses sensors, Internet, Cloud platforms, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence (AI). The size of the IoT network is getting bigger each day, like a giant robot. A few examples of IoT devices are- Smart home security systems
- Portable health monitors
- Smart factory equipment
- Shipping containers and logistics tracking
- Smart home appliances etc.
-
Quantum Computing
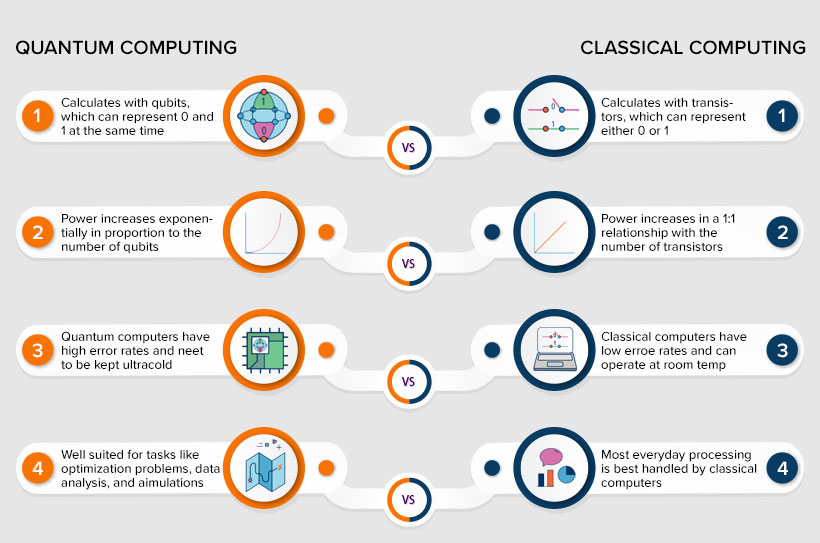
Quantum computing works based on the concept of quantum physics. It uses quantum bits, also known as qubits, as a basic unit of information. Quantum computers are better at performing complex tasks at high speed than any supercomputer can do. The properties of quantum physics, such as superposition and entanglement, are used in quantum computing.
- Superposition: The qubits use superposition to form a combination of all possible states. It’s like a coin flip; it could be heads or tails before landing. The possibilities are more with more qubit.
- Entanglement: This property is used to match up the results with the qubit. Once the qubits are entangled, the results of one qubit can be used to conclude the result of others. Likewise, complex problems can be solved by analysing more data.
The applications of quantum computing are drug development, financial modelling, weather forecasting, and climate change, cybersecurity, etc
-
Block Chain Technology
The blockchain is a decentralized database that differs from a regular database where the data is stored using a hash function. It stores data in the form of blocks, and the blocks are connected to form a data chain. When the data is stored in a blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to tamper, hack or trick the system. Even though various kinds of information can be stored in blockchain, it is mainly used as a transaction ledger. It is an emerging technology in cyberspace, as its full potential is not realized. Possible applications of blockchain technology will be fund transfers, sharing of medical data, personal identity security, voting mechanism, etc. It also forms the base for bitcoin, which could be the future of digital currency.
-
Encryption Technology
Encryption technology is gaining more importance in cyberspace. It is a process of converting the normal text into non-readable ciphertext. This prevents unauthorized persons from interpreting or tampering with the data. It is based on Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), where the encryption and decryption of data are done by Public-Private key distribution. There are numerous methods in data encryption that are Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA), Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), Triple DES (Data Encryption Standard, etc. Among these methods, QKD is highly secured as the QKD uses quantum mechanics for data encryption which cannot be cracked by normal computing.
Cyber Security Threats
Some of the most common cybersecurity threats are
-
Phishing Attacks
The cyber-attack carried out through spam emails is known as a phishing attack. This is because the usage of emails has become tremendous across cyberspace. But only a few emails are immune to cyber-attack, while most remain vulnerable. As a result, more people and organizations lose their data to hackers.
-
Ransomware Attacks
Among various malware attacks, ransomware has become dominant in recent years. This is because it not only gains access to confidential data but demands ransom from individuals or organizations. So, ransomware is turned into an illegal business, which is also successful. Moreover, the ransomware attack has moved from individuals working to organized crime, where many stakeholders are involved.
-
Cyber-attack on IOT Devices
The IOT devices are vulnerable to various kinds of cyber-attacks. The attack on the IOT devices includes DDoS attacks, unauthorized access to the data stored in the devices, adding the device to an illegal botnet, etc. As the IOT devices are spread geographically, a single attack will affect millions of devices.
-
Malwares Targeting Mobile Applications
Mobiles are handy devices, without which a day hardly passes by Millions of people worldwide use various mobile applications in their daily lives. However, in recent years, cybercriminals have targeted mobile applications where the applications tamper with malicious software. Once the app is installed, it spreads the malware that hacks the personal information from the device.
-
Data Breaches
The main aim of the cyber-attack is to steal the organization’s confidential data. Other than demanding ransom, this kind of attack is motivated by identity theft, damage to the institution’s reputation, espionage by rivals, etc.
Apart from this, various cybersecurity threats are emerging each year. Even though the evolving threats come under the above category, their potentials have improved recently. There are a few examples, such as the ‘Zero-day’ threat that avoids prior detection without any traces of digital signatures and ‘Advanced Persistent Threat,’ where the attackers hack the network and remain persistent despite software updates or system reboot.
Apart from this, various cybersecurity threats are emerging each year. Even though the evolving threats come under the above category, their potentials have improved recently. There are a few examples, such as the ‘Zero-day‘ threat that avoids prior detection without any traces of digital signatures and ‘Advanced Persistent Threat,’ where the attackers hack the network and remain persistent despite software updates or system reboot.
Current Trends in Cyber Security
-
Increased Use of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage stores data on the off-site location, accessed through the internet. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, many companies were forced to shift their process to remote work. It creates a huge threat to the organization as they use a cloud storage facility to store and share their data. Cybercriminals could use the vulnerabilities of misconfigured cloud security and unsafe home devices and networks to hack the data. While adapting to the cloud storage infrastructure, the organization should be aware of the security measures to prevent cyber-threat. With larger cloud storage adoption by companies, cybersecurity has also evolved in recent years.
-
Automation is Gaining Ground
With the increase in the communication networks in cyberspace, cyber threats are also increasing exponentially. This created a demand for cyber security experts in organizations. However, instead of looking for human assistance to eliminate the vulnerabilities in tools and technologies, organizations are trying to use automation to compete with cyber threats. The automation technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep learning can automatically detect the abnormalities in the data traffic to find the data breach without any human intervention.
-
Zero-Trust Principles are in Need
With the increase in network and data usage in an organization, it is important not to trust anyone without proper authentication. It is essential to verify the device, user, or entity before they can access the data. It is a continuous process that should be performed each time with every access permission. The zero-trust also includes limited access, where the access is granted only for needed resources, thus eliminating the data breach. It is not a stand-alone procedure, but a principle backed by software and technologies.
-
Responding Capacity
Cyber-attack such as ransomware attacks are common these days. Apart from being a threat, it has become a huge business on the dark web. The attackers can hack huge data and demand a ransom in return for data, or else the data would be sold for the bidders on the dark web. Not every cyber-attack can be prevented from happening. But timely response to the cyber threat can mitigate the severity of damage and help with a speedy recovery. Using the latest technologies to detect the threat early can help act at the initial state of a breach.
-
Supply Chain Risks
Most companies are dependent on vendors and service providers for their processes and data storage. This creates a huge vulnerability that criminals can utilize to carry on cyber-attacks. A single data breach of the vendors or service providers could affect several customers dependent on them. Moreover, it results in the company’s data loss, which is not caused by their mistake. Therefore, organizations should take necessary security measures with the vendors. It may include the vendor’s responsibility for any data breach, transparent and effective vendor security practices, mandating the vendors to have a cyber security framework, etc.
-
Call for Multi-Factor Authentication
The authentication procedure has been in use for a long time now. We use passwords for online applications such as email, social media accounts, e-commerce platforms to secure our personal information, a simple authentication process. In multi-factor authentication, multiple devices such as mobile phones and laptops are used to authenticate. For example, a remote working employee uses user id and passwords to login into the company’s network. But to access confidential files, more authentication such as mobile passcode should be entered to gain access. Recently, Microsoft has urged users to adopt app-based authentication instead of SMS or voice authentication, which is generally not encrypted and vulnerable to cyber-attack.
-
New Technologies and Devices are Adding on IOT (Internet of Things)
The number of devices using Bluetooth and Wi-Fi is rising day by day. These devices include smart plugs, fitness bands, baby monitors, home security devices, self-driving cars, home assistance devices. This adds to a huge amount of data that is vulnerable to cyber-attacks. This mandates the IOT industries to add cybersecurity features to their products.
Future of Cyber Security
Cyber security evolves with the emerging technologies in cyberspace.
-
Cybersecurity with AI
The expansion in the size of network communication in cyberspace generates a huge amount of data daily. As a result, the speed and volume of cyber-attacks increase, making it difficult to handle manual IT security operations. The latest technology of AI (Artificial Intelligence) comes to the rescue. It enables constant monitoring and speedy response to cyber-attacks.
-
Data Analytics
Big data collects large amounts of data with more complexity than traditional data management tools cannot manage. Big data is used to analyse a huge volume called big data analysis. It is efficient in interpreting and preventing cyber-attacks. In addition, it can detect abnormalities in data flow within the network.
-
Cloud Security
It is a set of policies and procedures backed by technology to secure the data and infrastructure of cloud storage. With the increase in the trend of remote working, the demand for cloud computing has increased exponentially, along which cloud security has also evolved.
-
Data Encryption
The encryption method has been used for a longer period, but its need has been raised in recent years. Data security using encryption technology is the best way to protect the data from hackers. In addition, data encryption using quantum computing is an emerging technology that makes it difficult for hackers to interpret the encoded data.
-
Cybersecurity With Blockchain
Blockchain technology can store a variety of data in a chain format that is hashed, making it impossible to tamper. As a result, this technology can store confidential data that should not be altered. It also allows for public access to data when needed.
Conclusion
Soon, the scope for cybersecurity will be bright. As more and more technologies are designed, the need for security is also pressed. Even though it attracts high-complex malware and cyber-attacks, it can be tackled by evolving software and technologies. Technology and cybersecurity are directly proportional, where the development of technology paves the way for the development of cybersecurity.