Exploring Cloud Security and Computing – Challenges, Mitigation and Penetration Testing
The technology developed has changed the way of functioning of the world. It has affected almost all the sectors, including communication, transport, energy, finance. It isn’t easy to find a field without the impact of technology. Business is no exception to this case, where adopting the trending technology measures the business’s success. One of the technologies named is cloud computing. Cloud computing is a booming technology that has a powerful impact in the business world. This document elaborates in detail about cloud computing, types of cloud computing, benefits, cloud security and cloud penetration testing.
What is Cloud Computing?
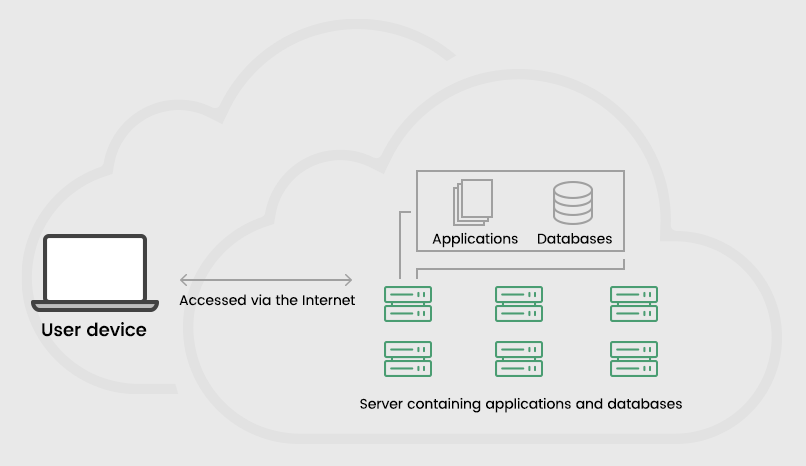
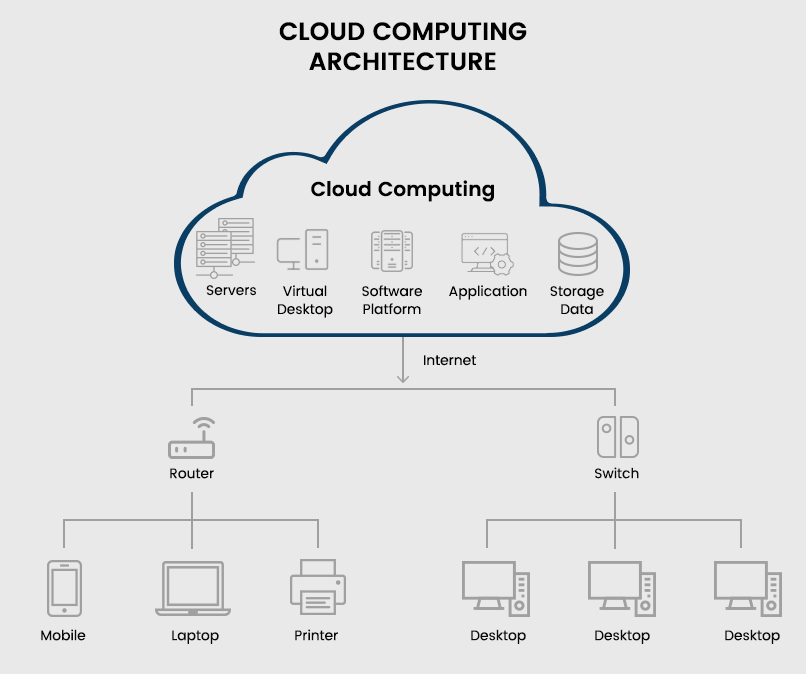
The computing infrastructure accessible through the internet is known as cloud computing. It includes all the computational facilities such as servers, storage, databases, applications, developing tools, networking competence, analytics, intelligence, etc. Cloud computing is provided as a service based on the requirements of the organizations. These computing services are delivered by the cloud service providers (CPS) with the help of data centres located remotely.
How Does it work?
The companies avail themselves of the cloud service on a rental basis that could be monthly or yearly. Therefore, it is essential to understand the working process of the cloud structure to realize the importance of cloud computing. Cloud computing is better understood with a clear example. Let us consider an IT company that works with systems and software to carry on its daily functions. It involves employees using computers and applications to complete the projects based on the requirement. If the company has its computing infrastructure, it must maintain all the computers and software used on its premises. If the employee increases, software and hardware infrastructure burden also increases with huge investment.
But in the case of cloud computing, all the computing needs, such as the software, data storage, server, database, etc., are provided by the cloud service provider. The company needs to provide the employees with computers to access the cloud interface, basically any device. Access to a cloud application is like using e-mail through the browser; anyone can use it with appropriate authentication. It eliminates the requirement of high features in the systems to run the applications remotely. Cloud computing reduces the huge financial burden of the company.
Cloud Computing Types
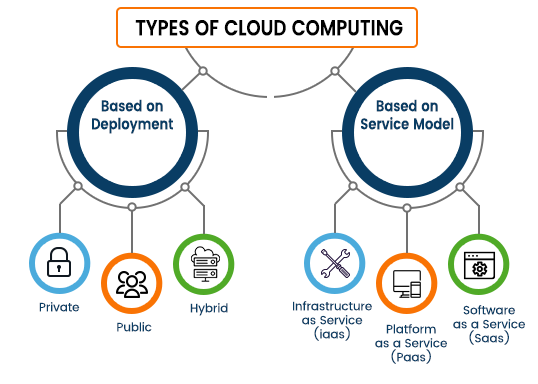
Cloud computing can be classified based on two criteria: the model and deployment. The facilities provided by the cloud service provider varies based on the cloud service model and implementation method chosen by the company. The cloud service model includes IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service) and SaaS (Software as a Service). In contrast, the deployment model is differentiated as public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud.
Cloud Service Model
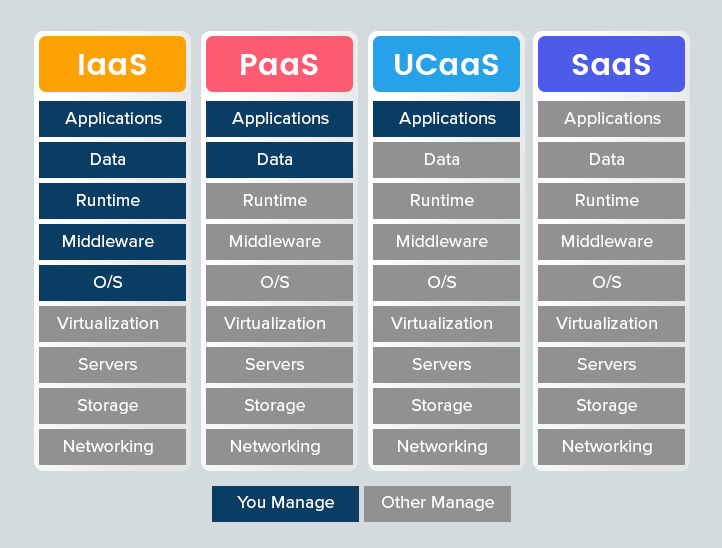
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
The IaaS model provides the user with the fundamental computing infrastructure required for software development and implementation. It includes physical or virtual servers, storage and networking, which can be accessed over the internet. The infrastructure as a service facilitates the software development from scratch, giving more control to the organization. This model is useful for companies that need to develop applications based on client requirements. As the service provider maintains the infrastructure, the speed of software development will improve with high efficiency and resilience. It also mitigates the financial burden of companies by minimizing the need for IT experts and physical on-premise infrastructures.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
The PaaS is the next level of service available in the cloud computing structure. In addition to the server, storage and networking of the IaaS model, the PaaS includes the software stacks, development tools, databases, middle and operating system. The cloud service providers maintain all these infrastructures on behalf of the company. Therefore, the developers can use the required software and tools to design, develop, test, deploy, maintain and update the applications with ease. The PaaS model is designed by leveraging the containers prototype. The containers are a stack of software packages that comprises a virtual operating system facilitating the usage of any OS service without any modification in the middleware.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
The SaaS model is the most widely used cloud computing model daily. In this model, the full software is available in the cloud to access the application on a monthly subscription with the provider. The company or the provider need to hire the application from the cloud service provider. The rest of the work is done by the cloud provider. As the service provider maintains the entire application, it facilitates the accessibility of the applications from any device like desktop, laptop, tablet, mobiles, etc. The SaaS applications can be accessed simply by the browser through the internet, irrespective of the device’s configuration. Here, the software updates will be frequent with improved interface and accessibility. It is the best model for both the user and the provider. The best examples of SaaS applications are Gmail, Netflix, Amazon, etc.
UCaaS (Unified Communication as a Service)
The UCaaS model, also known as Unified Communication as a Service, is the upcoming model which provides sustained communication and remote connectivity services. With the prevailing work from home situation, the UCaaS model proves to be an effective cloud service model by facilitating remote working through connectivity. It is possible by creating a secured and reliable working environment in the cloud. Many companies use the UCaaS model to make the employees from different locations work together as a team. It enhances productivity and encourages employees to work from remote locations. The popular example of the UCaaS model is Zoom, Microsoft teams, etc.
Cloud Deployment Model
Public Cloud
As the name suggests, the public cloud is developed and maintained by a third-party cloud provider. Both the physical and virtual cloud infrastructure is available over the public network, which is shared by the customers of the cloud service provider. Many companies choose the public cloud to reduce the cost of on-site infrastructure setup and maintenance. This model is suitable to process and store less sensitive information. The companies could move their partial process to the public cloud for flexibility and readily scalable features. Scaling the services helps to manage the resources based on the business requirement.
Private Cloud
The private cloud is the cloud infrastructure exclusive for only one entity. The cloud providers will have separate cloud networks for a single customer based upon their requirements. The private clouds provide high security, more control, and customized resources, along with flexibility and scalability features. For example, companies dealing with highly sensitive information such as customer data, intellectual property, health records, financial transactions, etc., can opt for a private cloud for high security and flexibility. The private cloud can use customer on-site data centres or separate off-site cloud infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud combines the features of the public cloud and the private cloud environment. It gives the flexibility of the public cloud and the security of the private cloud. Here, the organization can use the public environment for day-to-day business operations and the private cloud for managing sensitive information. It comes in handy for its efficiency in delivering new products and services with improved elasticity. It also secures critical data of the company. But it also creates difficulties in managing different cloud environments.
Multi-Cloud
The multi-cloud combines different cloud models from multiple cloud service providers. Most companies use a multi-cloud model to leverage various facilities provided by different service providers. The use of one or more public clouds and private clouds is known as hybrid multi-cloud. But increasing cloud types will increase the complexity of managing the multi-cloud environment because of divergent management tools and security arrangements.
Community Cloud
The community cloud infrastructure is like the public cloud environment. But in the case of a community cloud, only the group of organizations having a common field of operation can access the system and services. Third-party cloud providers can also handle the community cloud. An example of the community cloud is the healthcare industry, where the organizations can share the resources.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cost-Effective
The major advantage of cloud computing is the reduction in the operational cost of the business. Adopting a cloud environment will reduce the cost incurred by the infrastructure setup and maintenance of the on-premise computing framework. It also eliminates the need for large IT teams to manage the office infrastructure. As the cloud providers completely maintain the cloud services, the companies could save a huge chunk of money by leveraging the cloud platforms. Most cloud providers have a pay-as-go policy so that the companies can pay for what they use without any additional costs.
Resource Scalability
The other important aspect of cloud computing is the flexibility in scaling the resources according to the business requirements. Companies can use the services based on their current needs in cloud computing. The resources can be added or removed to match the sudden spike or drop in the business operation. In the case of on-premise infrastructure, huge investment is required to expand the operations, which will be a huge burden if there is a shortfall in business. The cloud service facilitates easy scaling of operation in parallel with the needs.
Remote Accessibility
The cloud server can be accessed globally, even from a remote village through the internet. Cloud computing serves a greater purpose of worldwide connectivity. Any device can access the cloud applications irrespective of the features and models. It also helps the business development by enabling easy data sharing through a secured network. The previous problem of device compatibility becomes obsolete with cloud applications.
Enhanced Cyber Security
Data security is one of the major concerns among companies that want to change their operations to the cloud. While in the case of on-site IT infrastructure, the entire security protocols come under the company’s responsibility. It makes the companies less considerate of cyber security measures that lead to data loss. But in cloud computing, the security comes under the service providers’ responsibility. The cloud hosting company has the required infrastructure and cloud security experts’ team, which works 24/7 to monitor the security of the cloud server.
Data Analysis
In the traditional business models, the data is stored in office premises, remote devices, or physical documents. It is a hectic task to retrieve any information from the pile of dis-oriented data. In this scenario, even though the company holds a huge amount of data, it becomes useless to the business development. The cloud server allows the storage of huge amounts of data arranged for easy information retrieval. Furthermore, it facilitates data analysis, which gives useful information from the available data that can be used for the future scope of the business.
Facilitates Team Work
In the present scenario of uncertainty, most of the adopted the work from the home model for uninterrupted business operation. The cloud network acts as a connecting platform to the employees that work from remote locations. It enables easy communication with the operational teams to share ideas and resources through a secured channel. The cloud model provides an optimal business solution for the growing number of remote employers.
Data Recovery
The cloud server enables easy and faster data recovery in unforeseen situations such as natural calamities, cyber-attacks, network error, etc. According to a report, 20% of cloud users claim the data recovery in four hours or less. In the case of on-site data storage, the recovery becomes a tedious job consuming from hours to days to recover the same data. As the data is stored in off-site locations, the data is safe from local problems or situations.
Frequent Software Updates
As the cloud provider is responsible for the database, server and applications, the cloud applications are updated automatically in regular intervals. It makes the cloud applications competent with the latest technology and security features. Thus, reducing the workload of the companies, which could contrate on the business functions rather than worrying about the software updates.
Storage Elasticity
Cloud storage is one of the services provided by cloud service providers. With the cloud provider taking care of the storage infrastructure, the companies can be relieved from the storage issues. The organization can also alter the storage sizes based upon the business needs. The company can pay the amount only for the used storage. It is advantageous when there is a fluctuation in the storage needs for the business operation.
Quality Management
Quality plays a key role in the success of any business. Therefore, it is essential to maintain the data quality and resources involved in the daily operations. Cloud storage ensures resource quality by storing all the data in a single format and placing them to be easily explored. It also enables multi-sharing of data in the standard format that helps track the data access. With cloud computing, quality management has become a painless task.
Mitigating Data Loss
With the traditional storage model, data loss is a greater threat, resulting in huge losses to the organization. Damage to the on-site infrastructure could result in permanent loss of critical data. However, using cloud storage facilities can mitigate it, which are virtual storage in off-site data centres. As a result, the data stored in the cloud database is unlikely to be lost. Further, the data can be accessed whenever needed.
Staying Ahead of Competitors
The usage of cloud facilities gives an added advantage over the competitors. The business that fails to leverage cloud technology will be outdated in the current market. In addition, cloud technology improves the efficiency of the business, which could result in huge success in the business. Therefore, the cloud service plays a key role in business development and helps stay ahead of the competitors.
Sustainable Technology
Cloud technology is otherwise known as sustainable technology as it reduces the waste of resources. It is mainly based on virtual infrastructure rather than a physical framework. Due to the implementation of cloud storage, the need for physical infrastructure is eliminated. It also reduces the waste of energy used in individual IT infrastructure, thus mitigating the carbon footprint, As multiple customers share the single cloud infrastructure. The only requirement for cloud access is a device with high-quality bandwidth.
What is Cloud Security?
Cloud security is a part of cyber security that helps secure the data and resources in the cloud computing environment. Cloud security comprises compliance, procedures and technology required to secure the cloud assets. It differs from traditional cyber security as the real data is stored in virtual storage (cloud storage). Therefore, a complete understanding of cloud computing is essential to implementing an effective cloud security framework.
In most cases, the cloud service provider takes the responsibility of securing the data in the cloud platform. But it is also the responsibility of the companies to secure their online assets from internal breaches and cyber-attacks. The security features in cloud computing differ based on the adopted cloud service model and deployment method.
Cloud Security Challenges and Mitigation
With the surge in cloud infrastructure adoption for business operations, security challenges are also increasing. The main reason for security concerns is the lack of understanding in the shared responsibility model between the CSP (cloud service provider) and the organization. The common security challenges that affect the cloud environment are listed below.
Data Breaches
The survey report of IDC, a global intelligence firm, suggests that data breach is at the top of the list of cloud security threats. Cloud storage involves high-speed data transfer over the internet, which creates a space for data breaches. A data breach could be detrimental to the business, affecting customer trust, regulatory compliance, revenue, and brand image. The major causes of a data breach include inefficient identity and access management, phishing attacks and insecure data transfer.
Preventive Measures
- using encryption technology like SSL Certificate can reduce the impact of data breaches and secure critical information.
- To control user access, organizations can use the principle of least privilege. For example, limiting access to critical resources helps mitigate the possibility of a data breach.
- The layer of security can be added through multi-factor authentication, eliminating unauthorized user access.
- Cyber hygiene helps to reduce data breach instances where proper removal and disposal of unused data can prevent data leaks.
Lack of Visibility
As the admins can operate the functions of the cloud servers over the network, there is a lack of visibility in the server management. As a result, it could lose control over the tools and resources, leading to security issues. The lack of visibility can create challenges such as employees using unauthorized applications and approved applications for malicious purposes. It creates a lack of governance that will attract more cyber security threats.
Preventive Measures
- A frequent risk assessment will help keep the cloud server control in check.
- Developing a framework for data access can create visibility in the cloud environment.
- Establishing and implementing regulatory compliance for cloud usage.
- Conducting an awareness program for access control, improving cloud visibility.
Account Hijacking
The exposure of credential information of the critical cloud account results in cloud hijacking. In this case, the hijacked account can carry out cyber-attacks resulting in a data breach, server downtime, etc. In addition, the hackers use various social engineering techniques to steal credentials from employees with privileged accounts. Therefore, the account hijacking harms the company’s business operations.
Preventive Measures
- Using Identity and Access Management controls to mitigate the possibility of suspicious account access.
- Maintaining critical and non-critical resources in a different environment limits access to critical resources.
- Monitor the user behaviour to spot malicious activities in the early stage.
- Create employee awareness regarding account hijacking prevention.
Misconfiguration
Cloud misconfiguration is one of the top reasons for vulnerability threats. In most cases, the misconfigurations are human errors like using the default settings, reusing the passwords, etc. The other reasons include excessive permissions, unused accounts, excess sharing, disabling standard security controls and more. However, the misconfiguration could lead to a cyber-attack, leading to data loss, including other losses that could be fatal to the business.
Preventive Measures
- Tracking and monitoring the data access management for suspicious activity. It helps in detecting the threats by tracking the changes in configurations.
- Creating a benchmark configuration and conducting a regular audit to check the configuration settings.
- Limiting the access to the authorized persons based on the need for resources for work. Frequent Revaluation of the designation and access permission of the employees.
Insider Threat
The threat is caused by the organization’s insiders, including employees, former employees, partners, and contractors who have access to sensitive data or privileged accounts. The insider threat could have a huge consequence on the business, even if it occurs accidentally. Therefore, it is the organization’s responsibility to take necessary measures to prevent insider threats from causing data leaks and security breaches in the cloud.
Preventive Measures
- Proper implementation of access control eliminates the abuse of privileged access.
- Identify and separate the critical resources secured with access control and authentication. Track the authorized personnel and monitor the data access to prioritize the critical resources. It helps to identify the threats beforehand.
- Split the privileged accounts from normal accounts for tracking purposes.
- Create a baseline access behaviour and mandate the employees to adhere to the baseline.
Insecure Interfaces and APIs
The UIs (User interface) and APIs (Application Programming Interface) are the most vulnerable part of the cloud infrastructure. Because of that, this acts as the communication platform between the customer and the CSP (Cloud Service Provider). But the security of the UI and API comes under the service provider’s responsibility. Where the security is integrated by the cloud provider that the user will monitor and manage, insecure UI and API will expose user account details and admin control.
Preventive Measures
- Using APIs designed according to the industrial standards with the visible framework.
- Limiting access to overriding tools allows the system, network, vulnerability management, and applications control changes.
- Follow proper API hygiene.
Lack of Cloud Security Experts
One of the primary reasons for all security challenges in cloud computing is the lack of cloud security experts. A sudden spike in the adoption of cloud computing for business has created a great demand for cloud experts. The cloud experts differ from the regular IT, as they require extensive knowledge in cloud computing to secure the cloud infrastructure and data. But there is a huge demand for cloud security experts resulting in poor maintenance of the cloud environment leading to vulnerability exposure. Cybercriminals can use it to perform a cyber-attack and steal critical information from the cloud server.
Mitigation
- The organizations can use third-party MSSP (Managed Security Service Provider) or cloud management company to handle the cloud infrastructure security. The advantage of leveraging the cloud security company is that it is equipped with security experts and tools to manage cloud security.
- The other way is to train the security professionals with the knowledge of cloud computing and the security tools and techniques to secure the cloud environment. The prolonged training with the right guidance will help the experts master cloud security.
What is Penetration Testing in Cyber Security?
Penetration is the process of inducing a simulated cyber-attack over the private network to find out the vulnerabilities present in the IT infrastructure. It is also a kind of ethical hacking, where the penetration test is pre-planned, and the outcome is analyzed to identify the vulnerabilities and fix them. With the help of advanced tools and techniques, one can also use it to check the implementation of the security framework in an organization.
Cloud Penetration Testing
The penetration test done in the cloud infrastructure is known as cloud penetration testing. The penetration test works with the shared responsibility of the CSP and the customer. There is a major difference between conducting a private and a cloud network penetration test. The surprise test can be conducted in the case of a private while in the cloud framework; a prior notice to the cloud service provider is essential to prevent any unforeseen impacts during the test.
Importance of Cloud Penetration Test
The penetration test plays a key role in maintaining the security in the cloud infrastructure. The pen-test identifies the vulnerabilities present in the network which the attackers can exploit. It helps to prevent cyber threats by fixing the vulnerabilities in the system. Despite detecting the loopholes, the pen-test can also be used for analyzing the efficiency of cloud security management. By identifying the lack of security, the organization can take remedial measures. Furthermore, preventing the cyber security threat can save the organization from huge financial losses and loss of customer trust and brand reputation. So, the penetration test facilitates uninterrupted business operations.
Types of Penetration Testing
- Black box penetration test– In this method, the penetration testers do not have access or knowledge of the organization’s cloud infrastructure.
- Grey box penetration test– Here, the penetration testers will have limited knowledge of the cloud framework and are granted restricted admin access based on the requirement.
- White box penetration test– The penetration testers are granted complete access to the cloud network, including the root-level access.
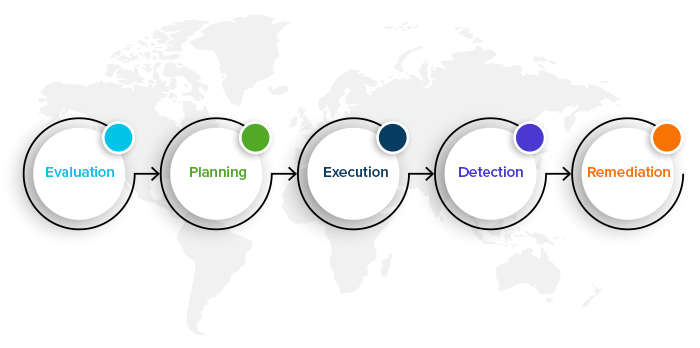
Steps Involved in The Cloud Penetration Testing
Evaluation
The first phase in conducting a penetration test is to evaluate the current cloud environment to identify the tested areas. Before starting a pen test, it is essential to spot the critical assets that could be an easy target for attackers. Without understanding the cloud structure, conducting a pen test will be a disaster that could create a new vulnerability. Proper evaluation of shared responsibility is also important for a successful pen test.
The organization should coordinate with the cloud provider to carve out the cloud security area under the organization’s responsibility. The company should give the service provider before protecting the other customers sharing the cloud platform from the simulated cyber-attack.
Planning
The next phase is to create a plan to conduct the penetrating test. As the pen test involves many stakeholders, it is essential to consider all the factors while planning the test. Even though the planning varies with each tester and the organization, some common steps are followed.
- Check with the cloud provider compliance to determine the types of tests permitted along with the allowed tools and techniques.
- Finalize the endpoints of the cloud, such as UI (user interface), APIs, and networks to be included in the testing.
- After confirming the test type, method, tools and landscape, the last step is to get approval from all the stakeholders such as CSP, clients, partners, etc.
Execution
After completing the planning phase, the testing team can execute the simulated cyber-attack. These executions are automated with little to no manual interference in most cases. The security team can use several tools for pen-test, such as AWS inspector, S3Scanner, Microburst, Azucar, Cloudspoilt etc. In addition, the testers can also use the dedicated testing tools from the cloud provider for simulation. Now comes the time to observe the penetration effects and monitor for vulnerabilities.
Detection
The simulation test will expose the vulnerabilities present in all the layers of security. It is the responsibility of the testing to verify the vulnerabilities to eliminate false alarms. Once the verification is complete, the next step is to prepare a detailed report on the identified vulnerabilities. The impact of the penetration test lies in the preparation of a vulnerability report so that it can be presented to the stakeholders. Without reporting the vulnerabilities, the pen test will waste time and resources.
Remediation
The next phase is to act upon the vulnerability report submitted by the IT security team. Detection without fixing is useless, so it is essential to identify the vulnerabilities. The remedies can be based on the nature of the vulnerabilities. Some can be rectified with minor coding, while others need specific tools and techniques. But, fixing the vulnerabilities can prevent the organization from the negative consequences of the unforeseen cyber-attack.
Conclusion
The organization can develop their business leveraging cloud computing technology. Thus, eliminating the several drawbacks in the previous business models. It also enables faster communication, easy data transfer, secured storage, frequent application development and updates, etc. Even though cloud adoption has all its benefits, it is also essential to keep cloud security in check to avoid cyber-attacks and data breaches. It is the shared responsibility of the Cloud service provider and the customer to secure the cloud infrastructure.